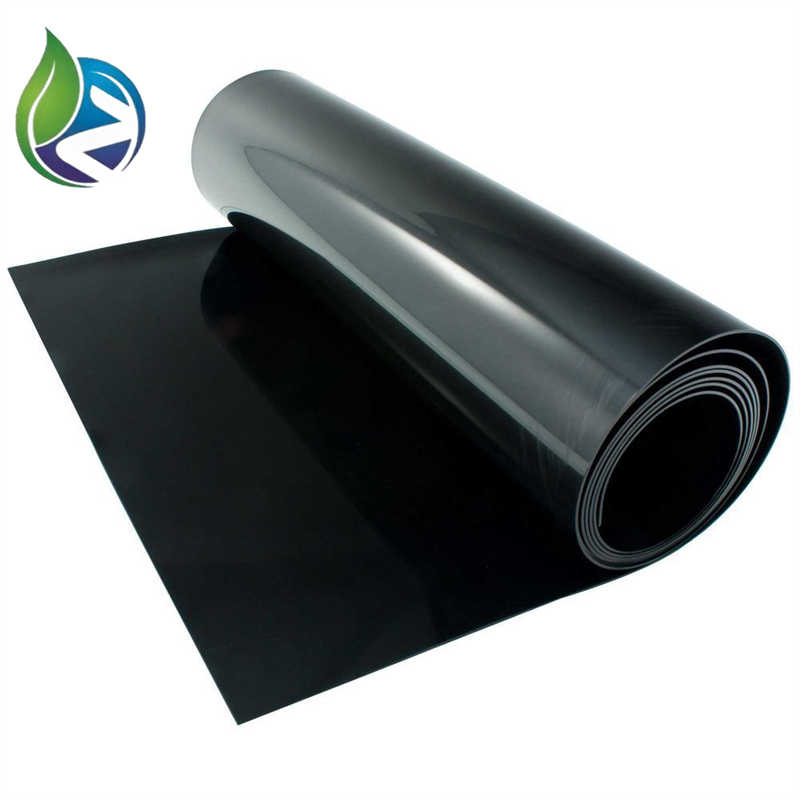
Low Density Polyethylene Geomembrane
Manufacturing Process
Low Density Polyethylene Geomembrane production follows a controlled, industrial extrusion process.
Raw material inspection and formulation batching
High-temperature extrusion using flat-die or blown-film extrusion lines
Online thickness monitoring via automatic gauge control
Calendering or air-ring cooling to stabilize sheet structure
Surface treatment and edge trimming
Roll winding under controlled tension
Finished product testing for mechanical and physical properties
Product Definition
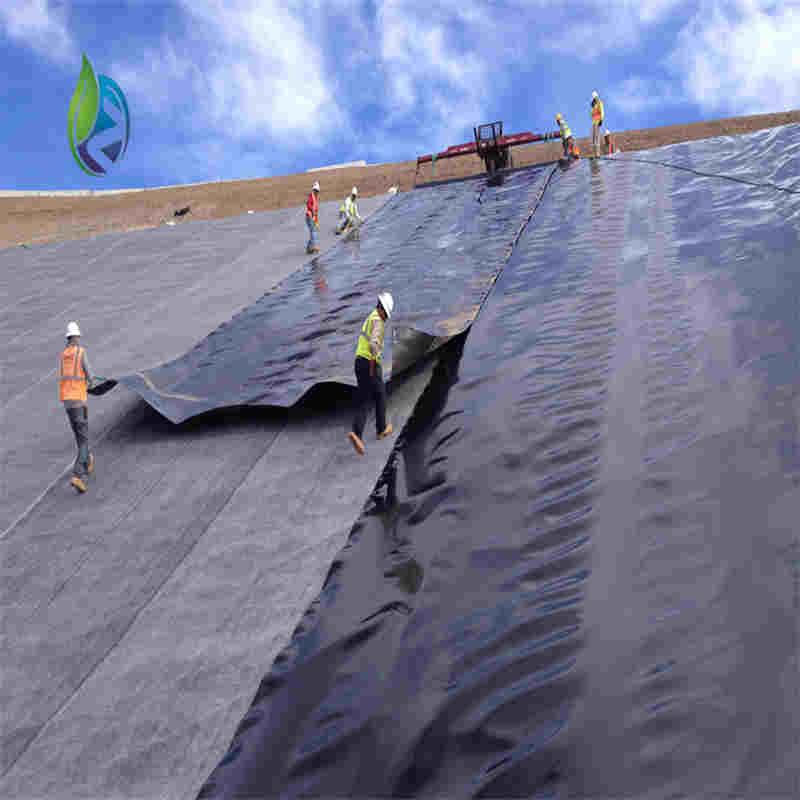
Low Density Polyethylene Geomembrane is a flexible polymeric barrier manufactured from LDPE resin, designed for seepage control, liquid containment, and environmental protection in civil, mining, agricultural, and industrial engineering projects requiring high elongation and adaptability.
Technical Parameters and Specifications
Low Density Polyethylene Geomembrane is engineered to meet common international geosynthetics performance requirements for containment and lining systems.
Thickness Range: 0.3 mm – 3.0 mm
Density: 0.915 – 0.930 g/cm³
Tensile Strength at Yield: ≥ 8 MPa
Tensile Strength at Break: ≥ 10 MPa
Elongation at Break: ≥ 600%
Puncture Resistance: ≥ 300 N
Tear Resistance: ≥ 150 N
Carbon Black Content: 2.0% – 3.0%
Oxidative Induction Time (OIT): ≥ 100 minutes
Service Temperature: -40°C to +60°C
Standard Roll Width: 5.8 m – 8.0 m
Roll Length: 50 m – 200 m
Structure and Material Composition
The structural composition of Low Density Polyethylene Geomembrane focuses on flexibility, durability, and resistance to environmental stress cracking.
LDPE Base Resin: Virgin polyethylene ensuring stable mechanical properties
Carbon Black: UV protection and long-term aging resistance
Antioxidants: Thermal and oxidative stability during service life
Processing Additives: Improve melt flow, thickness uniformity, and surface finish
Manufacturing Process
Low Density Polyethylene Geomembrane production follows a controlled, industrial extrusion process.
Raw material inspection and formulation batching
High-temperature extrusion using flat-die or blown-film extrusion lines
Online thickness monitoring via automatic gauge control
Calendering or air-ring cooling to stabilize sheet structure
Surface treatment and edge trimming
Roll winding under controlled tension
Finished product testing for mechanical and physical properties
Industry Comparison
| Material Type | Flexibility | Chemical Resistance | Stress Crack Resistance | Relative Cost | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low Density Polyethylene Geomembrane | High | Good | High | Medium | Landfills, ponds, canals |
| HDPE Geomembrane | Moderate | Excellent | Moderate | Medium-High | Hazardous waste, mining |
| LLDPE Geomembrane | Very High | Good | Very High | Medium | Irregular subgrades |
| PVC Geomembrane | Very High | Moderate | Low | Low-Medium | Decorative lining |
Application Scenarios
Low Density Polyethylene Geomembrane is widely specified by distributors, EPC contractors, and engineering firms for:
Municipal solid waste and industrial landfill lining systems
Wastewater treatment ponds and lagoons
Agricultural reservoirs and irrigation canals
Mining heap leach pads and tailings containment
Temporary containment and secondary spill protection
Water storage ponds for industrial facilities
Core Engineering Pain Points and Solutions
Uneven subgrade settlement: High elongation reduces liner cracking risk
Complex geometry installation: Flexible sheets adapt to slopes and curves
Seam failure risk: Compatible with hot wedge and extrusion welding systems
UV and aging exposure: Stabilized formulation extends outdoor service life
Risk Warnings and Mitigation Recommendations
Install protective geotextile layers over coarse or angular subgrades
Use certified welding technicians and calibrated equipment
Perform non-destructive seam testing on all welded joints
Avoid using non-certified recycled materials for critical containment
Control installation temperature to ensure proper seam fusion
Procurement and Selection Guide
Identify application type and chemical exposure conditions
Determine required thickness based on load and regulatory standards
Confirm compliance with ASTM, GRI, or equivalent specifications
Select roll dimensions based on site logistics and installation plan
Request third-party laboratory test reports
Evaluate supplier manufacturing capability and quality control
Assess availability of technical support and installation guidance
Engineering Case Application
In an industrial wastewater lagoon project, a 1.5 mm Low Density Polyethylene Geomembrane liner was installed over a compacted soil subgrade with nonwoven geotextile cushioning. The system accommodated differential settlement and temperature variation, achieving long-term seepage control and regulatory compliance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the typical service life? — 20–30 years under normal exposure.
Is it suitable for potable water storage? — Yes, with certified resin formulations.
Can it be welded on site? — Yes, using hot wedge or extrusion welding.
How does it differ from HDPE geomembrane? — LDPE offers higher flexibility.
What thickness is common for ponds? — Typically 1.0–1.5 mm.
Is UV resistance adequate? — Yes, with proper carbon black content.
Can it handle cold climates? — Installation is feasible above -10°C.
Is it resistant to acids and alkalis? — Resistant to most common chemicals.
Are custom roll sizes available? — Common for large-scale projects.
What quality tests are required? — Tensile, elongation, puncture, and seam tests.
Call to Action
For project-specific quotations, technical datasheets, engineering consultation, or material samples of Low Density Polyethylene Geomembrane, please submit your application details to our technical sales team.
E-E-A-T Author Credentials
This article is authored by a geosynthetics engineering professional with over 10 years of experience in geomembrane manufacturing, quality assurance, and EPC project support across environmental, infrastructure, and mining applications.