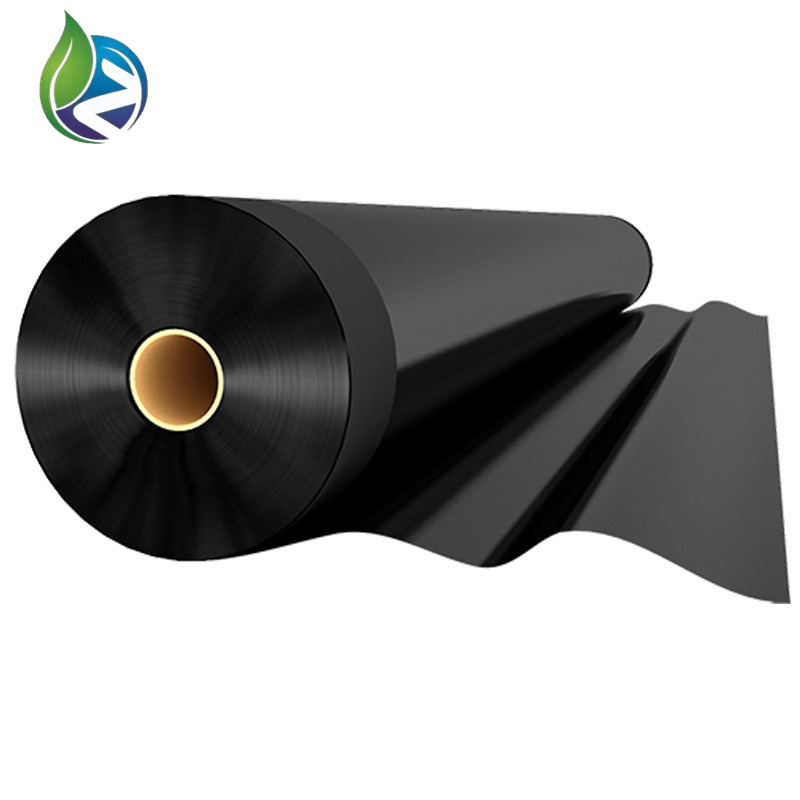
Geomembrane in HDPE
Manufacturing Process
Virgin HDPE resin drying and blending with masterbatch
High-output flat die or blown-film extrusion
Precision thickness control by automatic gauge systems
Surface texturing through embossing rollers (if required)
Roll cooling using controlled water and air systems
Inline inspection for gels, pinholes, and thickness deviations
Edge trimming, winding, and protective packaging
Product Definition
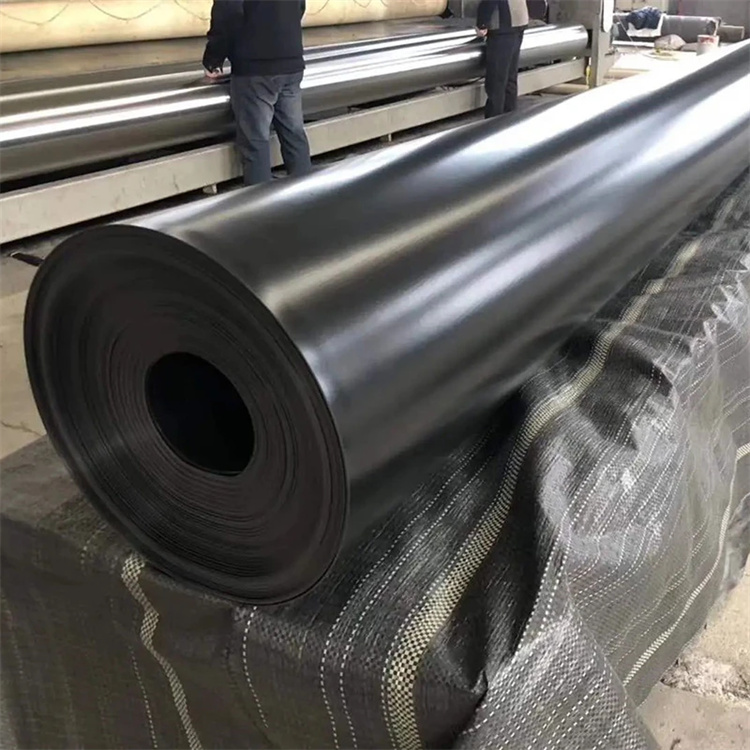
Geomembrane in HDPE is a high-density polyethylene impermeable lining material engineered to prevent liquid and gas migration in civil, environmental, and industrial containment systems. It provides long-term chemical resistance, mechanical strength, and dimensional stability for critical infrastructure applications.
Technical Parameters and Specifications
Base polymer: High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE)
Standard thickness: 0.5 mm, 0.75 mm, 1.0 mm, 1.5 mm, 2.0 mm, 2.5 mm
Density: ≥0.94 g/cm³
Tensile strength at yield: ≥17 MPa
Elongation at break: ≥700%
Puncture resistance: ≥600 N
Tear resistance: ≥250 N
Carbon black content: 2.0 – 3.0%
Oxidative induction time (OIT): ≥100 min (Std), ≥400 min (HP-OIT)
Width range: 3 m – 8 m
Typical roll length: 50 m – 200 m
Structure and Material Composition
Homogeneous HDPE polymer matrix
Integrated UV stabilizers (carbon black)
Thermal oxidation inhibitors
Smooth or textured surface options
Single-layer solid sheet structure
Optional co-extruded layers for enhanced surface friction
Manufacturing Process
Virgin HDPE resin drying and blending with masterbatch
High-output flat die or blown-film extrusion
Precision thickness control by automatic gauge systems
Surface texturing through embossing rollers (if required)
Roll cooling using controlled water and air systems
Inline inspection for gels, pinholes, and thickness deviations
Edge trimming, winding, and protective packaging
Industry Comparison
| Material Type | Chemical Resistance | Mechanical Strength | Service Life | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Geomembrane in HDPE | Excellent | High | 30–50+ years | Landfills, ponds, industrial lining |
| PVC Geomembrane | Moderate | Medium | 15–25 years | Decorative ponds, temporary liners |
| LDPE Liner | Good | Low | 10–20 years | Agricultural water storage |
| Clay Liner | Low | Low | Variable | Traditional landfill barriers |
Application Scenarios
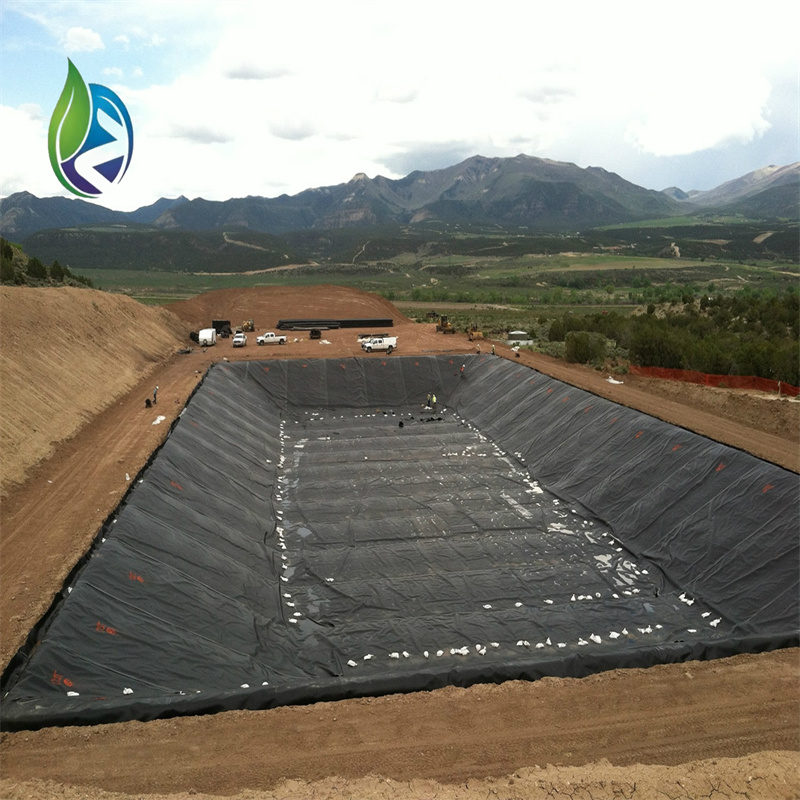
Landfill bottom liners and caps for EPC contractors
Industrial wastewater lagoons for project developers
Heap leach pads in mining operations
Canal and reservoir lining for water infrastructure projects
Secondary containment in chemical plants
Core Pain Points and Engineering Solutions
Leakage risk: Continuous HDPE sheet structure provides near-zero permeability.
Chemical degradation: HDPE resin resists acids, alkalis, and hydrocarbons.
Installation defects: Factory-controlled rolls minimize field seams.
Long-term aging: Carbon black and antioxidants extend service life.
Risk Warnings and Mitigation Measures
Risk of puncture from sharp subgrade – install protective geotextile layers.
Risk of seam failure – use certified hot wedge and extrusion welding.
Risk of UV exposure during storage – cover rolls and limit sunlight exposure.
Risk of thermal expansion – design adequate anchorage trenches.
Procurement and Selection Guide
Define containment type and chemical exposure conditions.
Select thickness based on hydraulic head and load calculations.
Verify compliance with ASTM and ISO geomembrane standards.
Request third-party test reports for OIT and density.
Confirm surface texture requirements for slope stability.
Evaluate factory production capacity and lot traceability.
Require welding procedure specifications (WPS) from installers.
Engineering Case Example
In a municipal landfill expansion project, Geomembrane in HDPE with a thickness of 2.0 mm was installed over a compacted clay layer across 85,000 m². The liner system demonstrated stable hydraulic performance and maintained seam integrity under continuous waste loading and leachate exposure.
FAQ
Q1: What is the primary function of Geomembrane in HDPE?
A: To provide impermeable containment of liquids and gases.
Q2: Can it be used for potable water reservoirs?
A: Yes, with food-grade compliant formulations.
Q3: What minimum thickness is typical for landfills?
A: Usually 1.5–2.0 mm, depending on regulations.
Q4: How are seams tested?
A: By non-destructive air pressure or vacuum box testing.
Q5: Is HDPE geomembrane flexible?
A: It is flexible but has a relatively high stiffness compared to LDPE.
Q6: What is the expected service life?
A: Typically more than 30 years in buried conditions.
Q7: Can it resist UV exposure?
A: Yes, due to carbon black stabilization.
Q8: What standards apply?
A: ASTM, ISO, and local environmental engineering standards.
Q9: Can installation be done in cold climates?
A: Yes, with controlled handling and preheating where required.
Q10: Is textured surface mandatory?
A: Only for steep slopes or low interface friction conditions.
Call to Action (CTA)
For detailed pricing, technical datasheets, welding guidelines, and engineering samples of Geomembrane in HDPE, submit a formal request including project drawings, loading data, and chemical exposure profiles for technical evaluation.
E-E-A-T Author Credentials
This technical document is prepared by a geosynthetics engineering specialist with over 15 years of experience in landfill, mining, and industrial containment projects, supporting EPC contractors, consultants, and infrastructure developers worldwide.