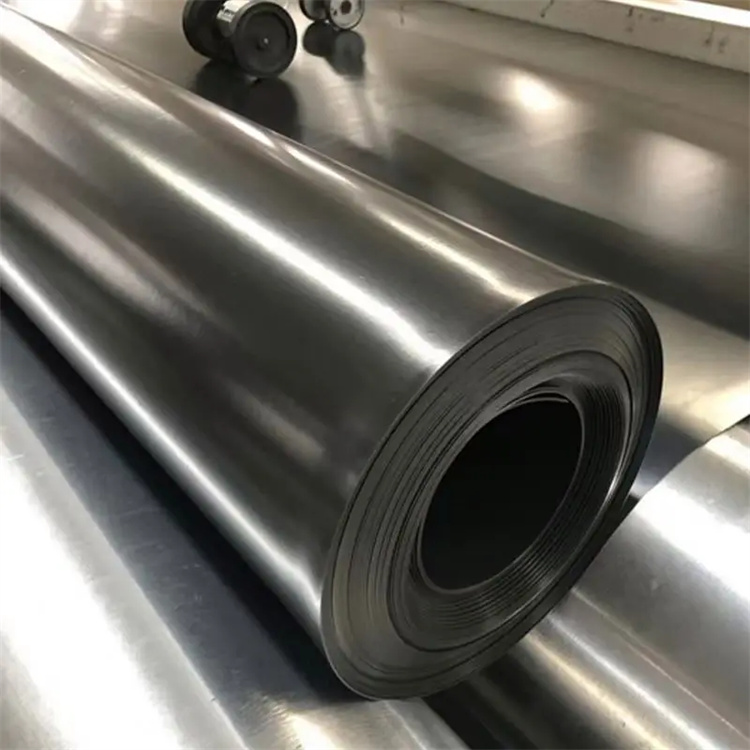
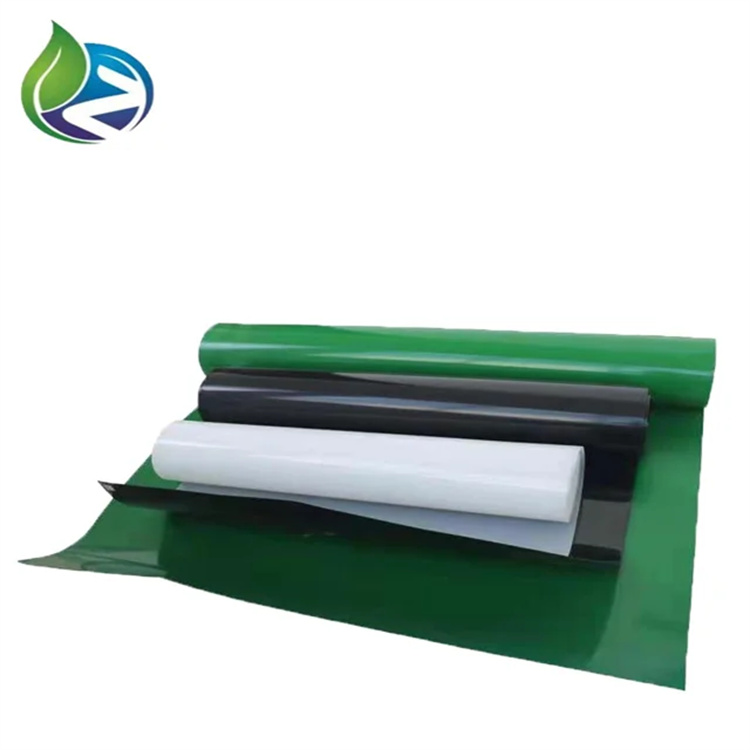
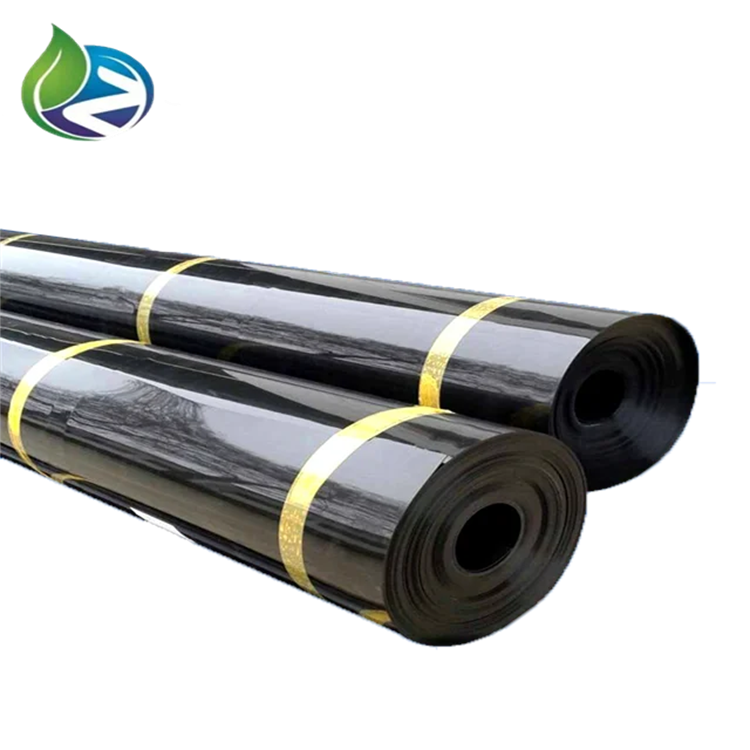
Black Hdpe Geomembrane
Manufacturing Process
The production of Black HDPE Geomembrane follows a controlled, engineering-grade manufacturing workflow:
Raw Material Preparation: Virgin HDPE resin blended with carbon black and stabilizers
Extrusion: Flat die or blown film extrusion equipment forms uniform sheets
Thickness Control: Automatic gauge control ensures tolerance within ±5%
Surface Treatment: Smooth or textured embossing based on application
Cooling & Annealing: Controlled cooling to reduce internal stress
Inspection & Testing: Mechanical, dimensional, and dispersion tests
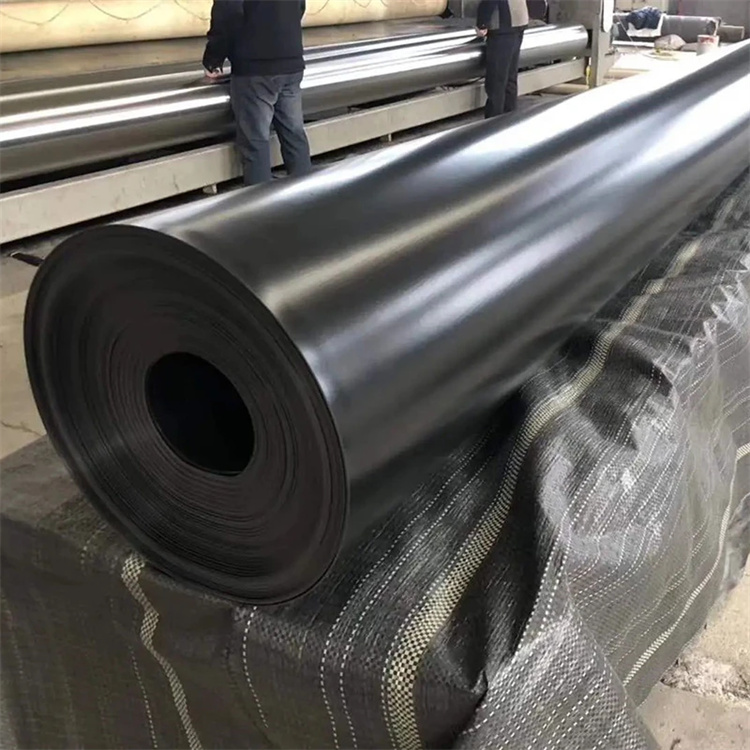
Rolling & Packaging: Packed for transport with moisture and UV protection
Product Definition
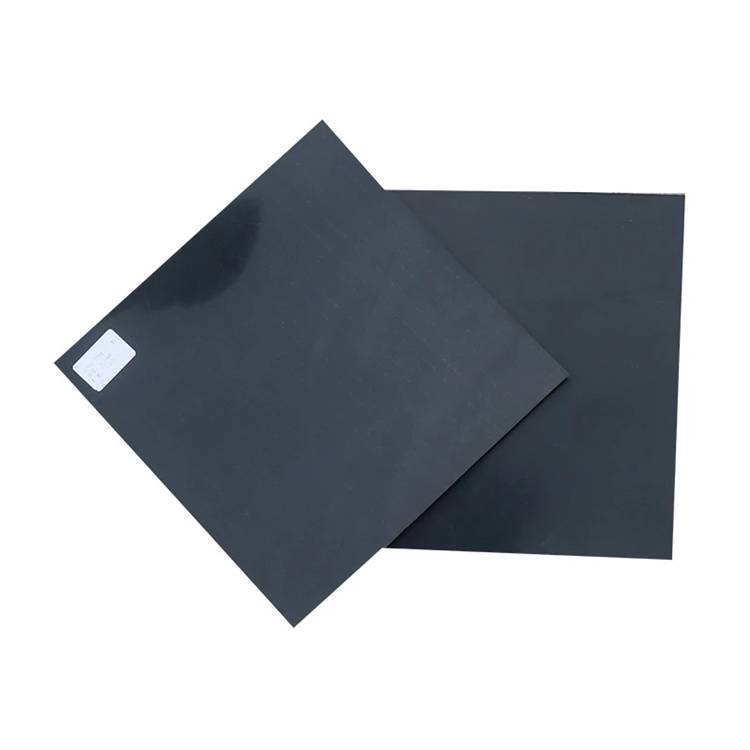
Black HDPE Geomembrane is a high-density polyethylene impermeable liner engineered for long-term containment, separation, and environmental protection applications. It offers excellent chemical resistance, UV stability, and mechanical strength for demanding civil and industrial engineering projects.
Technical Parameters and Specifications
All parameters below are aligned with commonly accepted international engineering practices and testing standards.
Material: High Density Polyethylene (HDPE)
Color: Black (carbon black content 2.0%–3.0%)
Thickness Range: 0.5 mm – 3.0 mm
Density: ≥ 0.94 g/cm³
Tensile Strength at Yield: ≥ 15 MPa
Elongation at Break: ≥ 700%
Puncture Resistance: ≥ 500 N
Carbon Black Dispersion: Grade 1–2
Service Temperature: -40°C to +60°C
Expected Service Life: > 50 years (proper installation)
Structure and Material Composition
Black HDPE Geomembrane is designed as a homogeneous or co-extruded polymer sheet with the following structure:
Primary Resin Layer: Virgin HDPE resin providing mechanical strength
Carbon Black Additive: UV protection and oxidation resistance
Antioxidant Package: Thermal and long-term aging resistance
Optional Textured Surface: Enhanced friction for slope stability
Manufacturing Process
The production of Black HDPE Geomembrane follows a controlled, engineering-grade manufacturing workflow:
Raw Material Preparation: Virgin HDPE resin blended with carbon black and stabilizers
Extrusion: Flat die or blown film extrusion equipment forms uniform sheets
Thickness Control: Automatic gauge control ensures tolerance within ±5%
Surface Treatment: Smooth or textured embossing based on application
Cooling & Annealing: Controlled cooling to reduce internal stress
Inspection & Testing: Mechanical, dimensional, and dispersion tests
Rolling & Packaging: Packed for transport with moisture and UV protection
Industry Comparison
| Material | Permeability | Chemical Resistance | Service Life | Typical Cost Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Black HDPE Geomembrane | Extremely Low | Excellent | 50+ Years | Medium |
| LDPE Geomembrane | Low | Moderate | 25–30 Years | Low |
| PVC Liner | Low | Limited | 15–20 Years | Medium |
| Clay Liner | Moderate | Poor | Variable | Low |
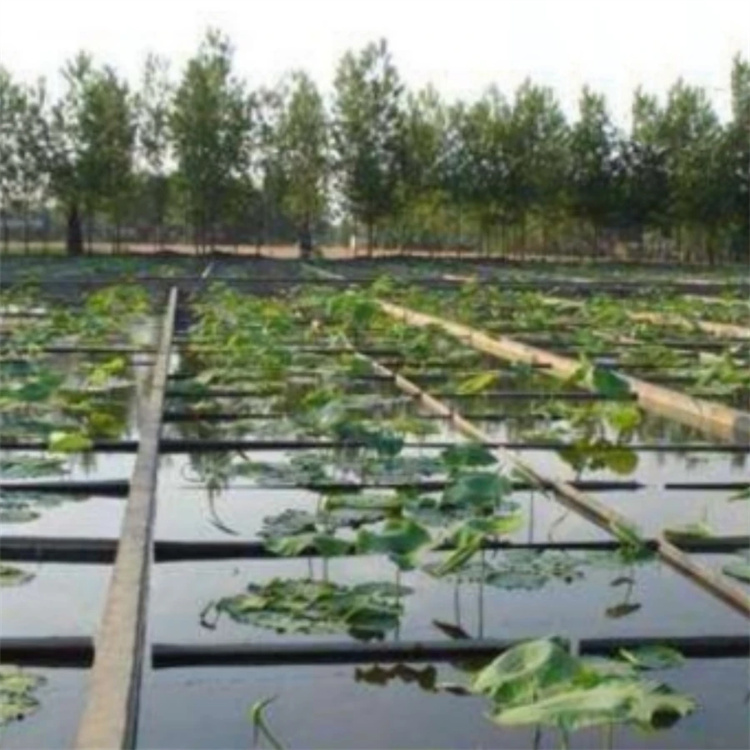
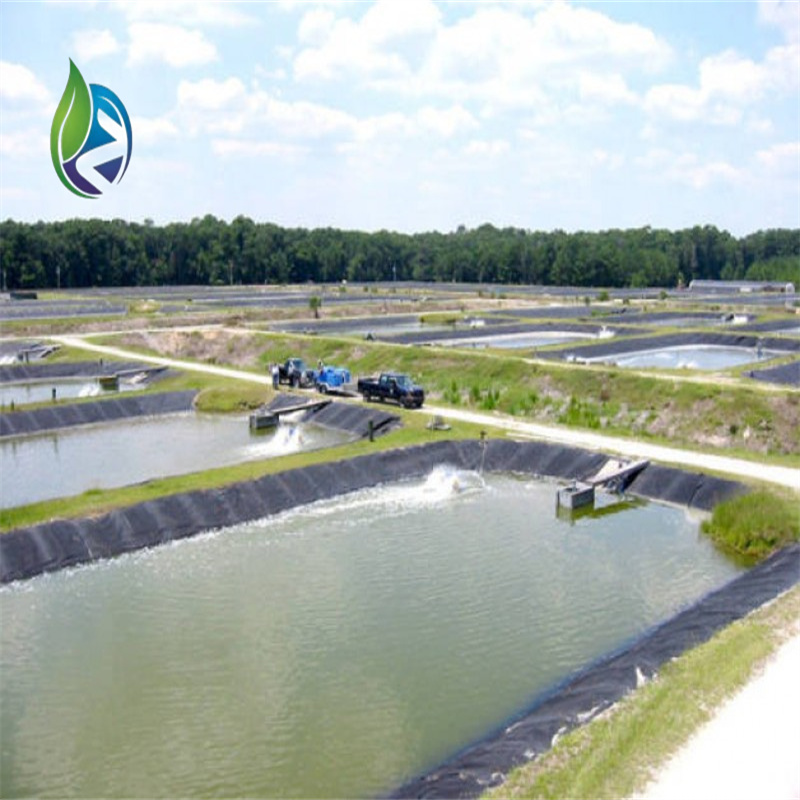
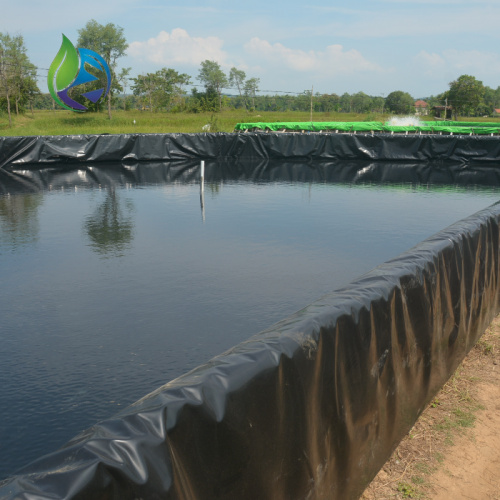
Application Scenarios
Black HDPE Geomembrane is widely used across infrastructure and environmental engineering sectors:
Landfill bottom liners and capping systems
Mining leach pads and tailings dams
Wastewater treatment lagoons
Water reservoirs and canals
Industrial containment ponds
Agricultural irrigation storage
Core Pain Points and Solutions
Leakage Risk: Solved by ultra-low permeability HDPE structure
UV Degradation: Carbon black stabilizes long-term outdoor exposure
Chemical Attack: HDPE resists acids, alkalis, and hydrocarbons
Slope Instability: Textured geomembranes improve interface friction
Risk Warnings and Mitigation Measures
Avoid subgrade sharp objects; use protective geotextile
Ensure certified welding technicians for seam integrity
Control thermal expansion during installation
Perform non-destructive seam testing before commissioning
Procurement and Selection Guide
Define application environment and chemical exposure
Select appropriate thickness based on load conditions
Choose smooth or textured surface as required
Verify compliance with project specifications
Request batch testing reports
Confirm installation support and welding guidance
Engineering Case Example
In a municipal landfill expansion project, a 2.0 mm Black HDPE Geomembrane was installed over a compacted clay layer with protective geotextile. Dual-track hot wedge welding was applied, followed by air pressure testing. The system achieved zero leakage during commissioning and has remained operational under leachate exposure for over eight years.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What thickness is most common?
A: 1.5–2.0 mm for containment projects.Q2: Is it suitable for drinking water?
A: Yes, with appropriate certification.Q3: Can it be welded onsite?
A: Yes, using hot wedge or extrusion welding.Q4: How long does installation take?
A: Depends on area and complexity.Q5: Does black color affect performance?
A: Yes, improves UV resistance.Q6: Is textured always better?
A: Only for slope applications.Q7: Can recycled HDPE be used?
A: Not recommended for critical containment.Q8: What testing is required?
A: Tensile, puncture, dispersion, seam tests.Q9: How is it transported?
A: Rolled and wrapped for protection.Q10: Can it be repaired?
A: Yes, via localized patch welding.
Call to Action
For project-specific quotations, detailed technical datasheets, or engineering samples of Black HDPE Geomembrane, please submit your requirements to our technical sales team for professional support.
E-E-A-T Author Credentials
This article is prepared by a materials engineering team with over 15 years of experience in geosynthetics manufacturing, quality control, and large-scale civil engineering applications, supporting EPC contractors and international distributors worldwide.