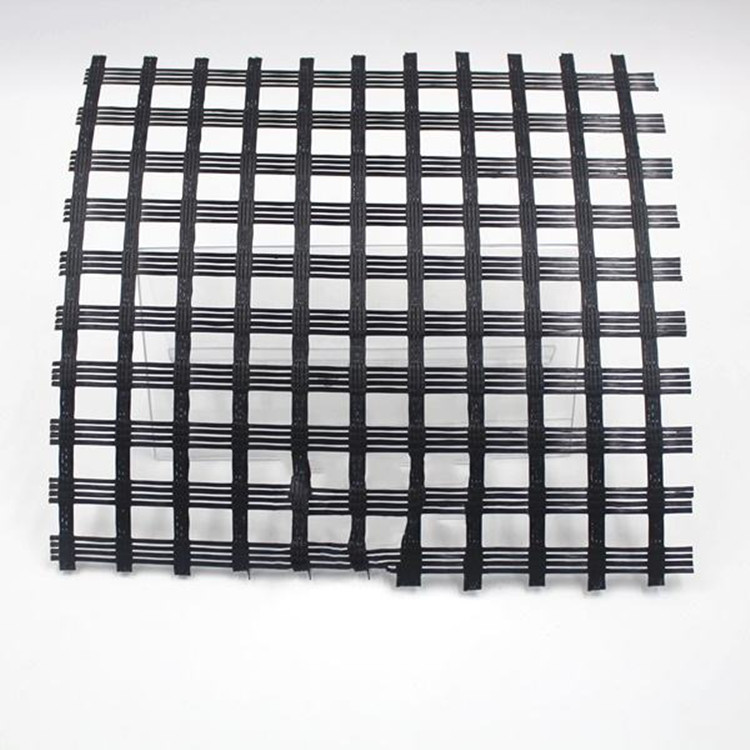
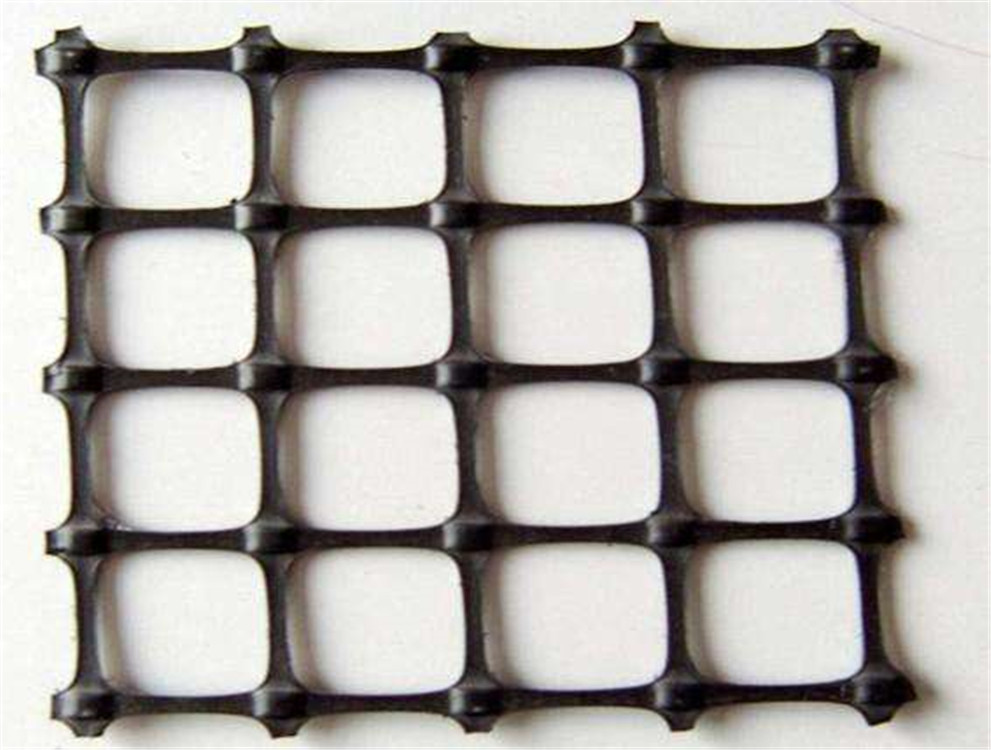
The Difference Between Plastic Geogridand Glass Fiber Geogrid
The Difference Between Plastic Geogrid and Glass Fiber Geogrid
In the field of civil engineering and construction, geogrids are widely used for soil reinforcement, road construction, and slope stabilization. Two of the most commonly used types of geogrids are plastic geogrids and glass fiber geogrids. Both materials serve similar purposes but have distinct characteristics and applications. In this article, we will explore the key differences between plastic geogrid and glass fiber geogrid to help you determine which material is best suited for your project.
What is a Geogrid?
A geogrid is a type of geosynthetic material that is used to reinforce soils and other granular materials. Geogrids are typically made from polymers or synthetic materials, and their primary function is to improve soil stability, reduce settlement, and increase load-bearing capacity. They are widely used in road construction, railway tracks, retaining walls, and landfills, among other civil engineering applications.
Geogrids come in various types, including plastic geogrids and glass fiber geogrids, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages.
1. Material Composition
The primary difference between plastic geogrid and glass fiber geogrid lies in the material from which they are made.
Plastic Geogrid: As the name suggests, plastic geogrids are made from high-density polyethylene (HDPE), polypropylene (PP), or other plastic-based materials. These materials provide the geogrid with high flexibility, resistance to chemical reactions, and durability, making them ideal for applications where soil movement or expansion is expected.
Glass Fiber Geogrid: Glass fiber geogrids are made from woven or nonwoven glass fibers, often combined with resins for added strength and durability. These geogrids offer excellent tensile strength and are highly resistant to high temperatures and UV degradation. Glass fiber geogrids are ideal for applications that require high performance in terms of load distribution and resistance to harsh environmental conditions.
The material composition of both types of geogrids determines their performance and suitability for specific applications. Plastic geogrids are more flexible and resistant to moisture, while glass fiber geogrids are stronger in tension and better suited for heavy load-bearing applications.
2. Tensile Strength and Load-Bearing Capacity
Both plastic geogrid and glass fiber geogrid are designed to improve the strength of soil and other materials, but their tensile strength and load-bearing capacities differ.
Plastic Geogrid: Plastic geogrids generally offer high tensile strength, which helps in distributing loads evenly across the reinforced area. However, they may not provide as much load-bearing capacity as glass fiber geogrids in extreme conditions. They are suitable for moderate load applications where flexibility and ease of installation are more critical than extreme strength.
Glass Fiber Geogrid: Glass fiber geogrids are known for their superior tensile strength and ability to withstand heavy loads. This makes them ideal for use in applications such as road stabilization, rail track reinforcement, and other heavy-duty construction projects. The high tensile strength of glass fiber geogrids ensures that they can handle large loads without deformation or failure.
While plastic geogrids offer flexibility and moderate load-bearing capacity, glass fiber geogrids excel in environments where extreme tensile strength is required.
3. Durability and Resistance
Durability and resistance to environmental factors are critical when selecting a geogrid for a particular application.
Plastic Geogrid: Plastic geogrids are resistant to moisture, chemicals, and biological degradation. They are well-suited for applications in moist or aggressive environments, such as drainage systems or landfill liners. However, they may not perform as well in high-temperature environments, as excessive heat can weaken the plastic material over time.
Glass Fiber Geogrid: Glass fiber geogrids are highly resistant to high temperatures, UV radiation, and chemical exposure. They are less affected by the environment compared to plastic geogrids, making them ideal for use in challenging conditions, such as in areas with extreme weather, heavy traffic, or exposure to chemicals.
In terms of durability and resistance, glass fiber geogrids offer superior performance in harsh environments, while plastic geogrids are better suited for moist, chemically neutral areas.
4. Flexibility vs. Rigidity
The flexibility or rigidity of a geogrid plays a crucial role in how it performs under different conditions.
Plastic Geogrid: Plastic geogrids are generally more flexible compared to glass fiber geogrids. This flexibility allows them to adapt to soil movements and shifts without cracking or breaking. They are ideal for use in areas where soil settlement or expansion is expected, such as in road construction and embankments.
Glass Fiber Geogrid: Glass fiber geogrids are more rigid and less flexible than plastic geogrids, which makes them suitable for applications where high tension and load-bearing capacity are required. Their rigidity makes them excellent for stabilizing soils under extreme pressure, but they may not be as effective in environments where the soil is expected to shift or move.
If flexibility is a priority for your project, plastic geogrids are the better choice, while glass fiber geogrids are more appropriate for rigid, load-bearing applications.
5. Cost Considerations
The cost of geogrids can vary significantly depending on the material used, manufacturing process, and the specific application.
Plastic Geogrid: Plastic geogrids are generally more affordable than glass fiber geogrids, making them a popular choice for budget-conscious projects. They offer good performance in moderate load-bearing applications and are more cost-effective in situations where high tensile strength and environmental resistance are not a priority.
Glass Fiber Geogrid: Glass fiber geogrids tend to be more expensive due to their superior tensile strength, durability, and resistance to harsh environmental conditions. However, their higher initial cost may be justified in high-load applications where long-term performance and stability are critical.
When it comes to cost, plastic geogrids provide an economical solution for many projects, while glass fiber geogrids may be the better investment for demanding, high-stress environments.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Plastic Geogrid and Glass Fiber Geogrid
Both plastic geogrids and glass fiber geogrids offer distinct advantages and are suitable for different applications in civil engineering and construction. The choice between the two depends on factors such as tensile strength, durability, environmental conditions, flexibility, and cost.
Plastic Geogrid: Best for moderate load-bearing projects, flexible environments, and cost-effective solutions.
Glass Fiber Geogrid: Ideal for heavy-duty applications requiring high tensile strength, resistance to high temperatures, UV exposure, and extreme environmental conditions.
By carefully considering the specific requirements of your project, you can select the right type of geogrid to enhance the performance, stability, and longevity of your construction work.
Glass fiber geogrid : Plastic geogrid: