The Advantage of Geocell Room Planting Grass Slope Protection
Product Definition: Geocell Room Planting Grass Slope Protection
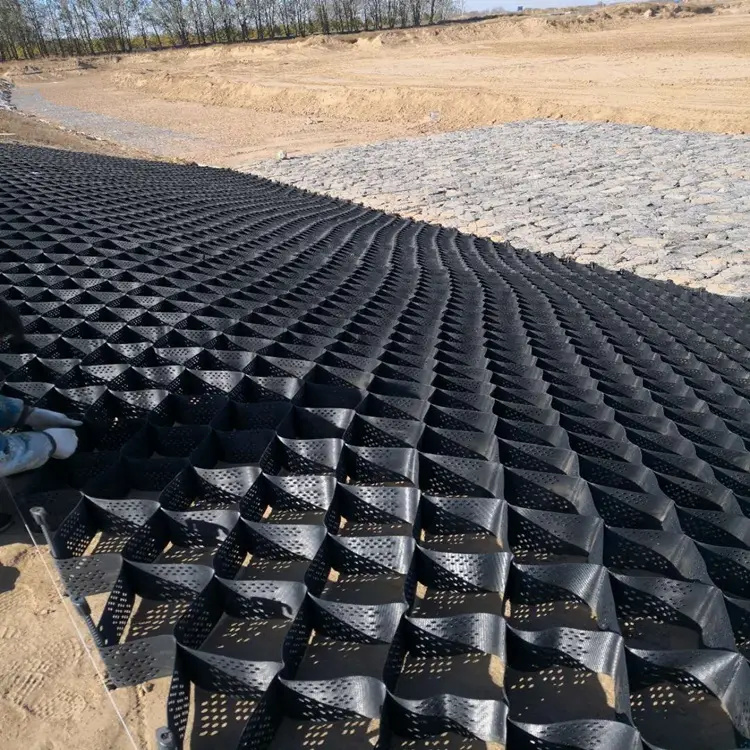
Geocell room planting grass slope protection is a composite ecological slope stabilization system that combines three-dimensional HDPE geocell confinement with soil and vegetation. It enhances slope stability, controls erosion, and supports long-term ecological restoration through mechanical reinforcement and biological root anchoring.
Technical Parameters and Specifications
The following technical parameters are commonly applied in highway, municipal, and landscape slope protection projects. Specifications may be adjusted based on slope angle, soil type, and load conditions.
| Parameter | Typical Range |
|---|---|
| Material | High Density Polyethylene (HDPE) |
| Cell Height | 50 mm / 75 mm / 100 mm / 150 mm |
| Cell Size (Expanded) | 300–500 mm |
| Sheet Thickness | 1.1–1.8 mm |
| Tensile Strength | ≥20 MPa |
| Peel Strength at Seam | ≥100 N/cm |
| UV Resistance | ≥80% strength retention (after 500 h) |
| Service Life | ≥25 years (buried condition) |
Structure and Material Composition
Geocell room planting grass slope protection adopts a modular honeycomb structure that integrates mechanical confinement and ecological planting.
HDPE Geocell Strips: Extruded polymer sheets with high tensile and environmental resistance
Ultrasonic or Thermal Welded Nodes: Ensure structural integrity under slope loading
Three-Dimensional Cell Network: Provides lateral confinement for soil and root systems
Vegetation Fill: Topsoil mixed with grass seeds or turf for biological reinforcement
Manufacturing Process and Engineering Control
Manufacturing Steps
HDPE resin selection and drying
Flat sheet extrusion with thickness control
Precision punching and surface texturing
Ultrasonic or hot-melt welding to form geocell strips
Accordion folding and dimensional calibration
Mechanical strength and seam peel testing
Packaging and batch traceability marking
Key Production Equipment
High-output HDPE extruders
Automatic welding machines
Computer-controlled tensile testers
UV aging and environmental testing chambers
Industry Comparison
Comparison between geocell room planting grass slope protection and conventional slope protection methods:
| Aspect | Geocell + Grass | Shotcrete Slope | Stone Pitching |
|---|---|---|---|
| Erosion Control | Excellent | Good | Medium |
| Ecological Restoration | High | None | Low |
| Structural Flexibility | High | Low | Low |
| Construction Speed | Fast | Medium | Slow |
| Life-Cycle Cost | Low | High | Medium |
Application Scenarios
The advantage of geocell room planting grass slope protection is most evident in projects requiring both stability and ecological performance:
Highway and railway embankment slopes
Riverbank and reservoir slope protection
Municipal road cut slopes
Industrial park and logistics park landscaping
Mine rehabilitation and landfill closure slopes
Core Pain Points and Engineering Solutions
Slope soil erosion during rainfall: Geocell confinement prevents surface soil loss and runoff concentration
Poor vegetation survival: Cellular structure retains moisture and nutrients for root growth
Shallow landslide risk: Combined mechanical and biological reinforcement improves shear resistance
High maintenance cost: Long-term stability reduces repair frequency
Risk Warnings and Mitigation Measures
Ensure adequate anchoring at crest and toe of slope
Control fill compaction to avoid cell deformation
Select grass species suitable for local climate
Avoid prolonged UV exposure before backfilling
Provide temporary drainage during vegetation establishment
Procurement and Selection Guide
Assess slope gradient, height, and soil conditions
Determine required cell height and sheet thickness
Confirm tensile and seam strength requirements
Select UV-resistant HDPE grade
Evaluate compatibility with planting soil and vegetation
Request laboratory test reports and certifications
Review supplier engineering support capability
Engineering Case Study
In a municipal highway project involving a 12 m high soil slope with a gradient of 1:1.5, geocell room planting grass slope protection with 100 mm cell height was installed over 8,500 m². After two rainy seasons, monitoring showed no surface erosion, vegetation coverage exceeded 95%, and maintenance costs were reduced by approximately 40% compared to traditional stone pitching.
FAQ: Technical and Engineering Questions
Is geocell slope protection suitable for steep slopes? Yes, with proper anchoring and design.
Can it be used in cold climates? HDPE geocells maintain flexibility at low temperatures.
What soil is recommended for filling? Fertile topsoil mixed with sand is preferred.
How long does vegetation establishment take? Typically 4–8 weeks depending on climate.
Is irrigation required? Temporary irrigation is recommended during early growth.
Does it replace structural retaining systems? It is suitable for shallow slope stabilization, not deep retaining walls.
What is the expected service life? Over 25 years under buried conditions.
Can it be combined with geotextile? Yes, separation layers are often used.
Is maintenance required? Minimal after vegetation is established.
Does it comply with international standards? Commonly aligned with ASTM and ISO geosynthetics standards.
Request Quotation or Technical Documentation
For project-specific designs, technical datasheets, laboratory test results, or engineering samples of geocell room planting grass slope protection, procurement and engineering teams are invited to submit formal requests for evaluation and quotation.
E-E-A-T: Authoritative Technical Background
This content is developed by professionals specializing in geosynthetics engineering, slope stabilization, and ecological restoration, with extensive experience supporting EPC contractors, infrastructure developers, and international distributors across transportation and environmental projects.