The "3D Grid Structure" of Geocells: How Grid Size and Height Determine Their Constraint Efficiency?
The "3D Grid Structure" of Geocells: How Grid Size and Height Determine Their Constraint Efficiency?
Geocells have become a critical solution in modern geotechnical engineering, offering superior soil stabilization, erosion control, and load distribution capabilities. Understanding how the 3D grid structure of geocells affects performance is essential for international B2B buyers seeking high-quality solutions for infrastructure, road construction, and slope reinforcement projects.
Industry Background and Market Overview
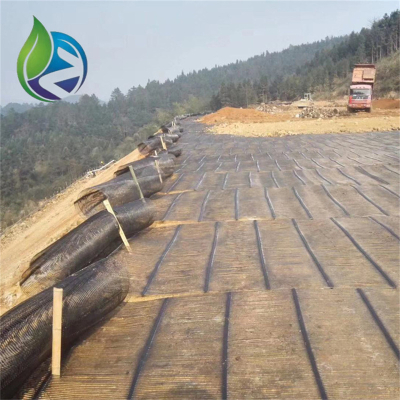
The global geocell market has experienced consistent growth, driven by increasing infrastructure investments and environmental concerns related to soil erosion and slope stability. Geocells, particularly those with a 3D grid structure, are widely used in highways, embankments, retaining walls, and green infrastructure projects due to their efficient load-bearing and soil confinement properties.
Recent market data indicates that geocells with higher heights and optimized grid sizes can significantly improve soil confinement efficiency, resulting in reduced material costs and longer service life. For international buyers, sourcing geocells with precise structural specifications is vital to ensure performance in diverse environmental conditions.
Technical Analysis: Grid Size and Height in Geocells
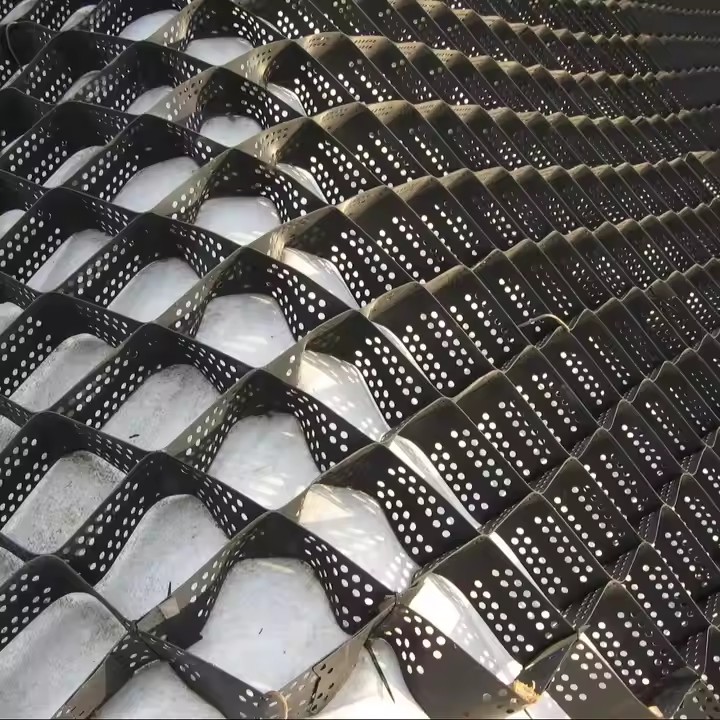
Grid Size and Soil Confinement
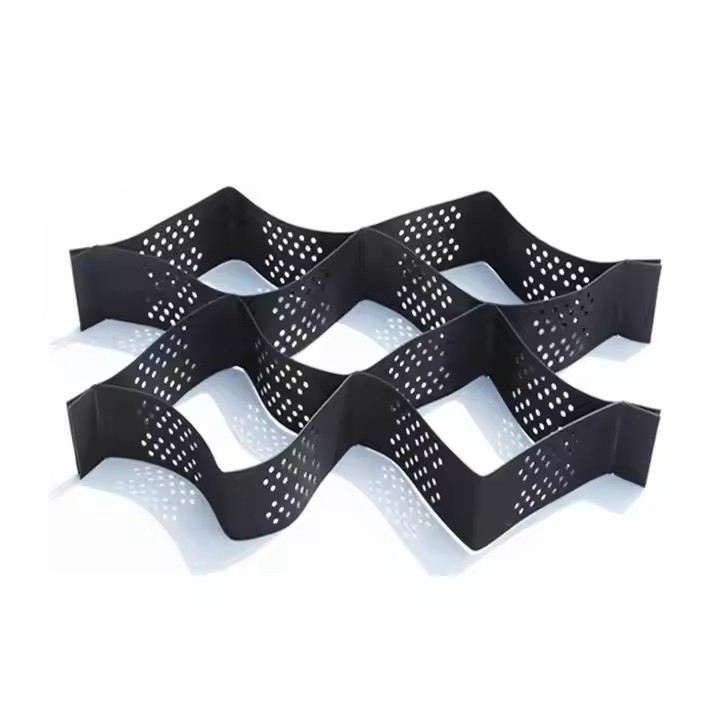
The grid size of a geocell directly impacts its ability to constrain infill material. Smaller grid openings enhance lateral confinement, reducing soil displacement under load. Conversely, larger grid sizes allow for easier infill placement but may reduce constraint efficiency. Choosing the appropriate grid size depends on project-specific factors such as soil type, load requirements, and slope gradient.
Geocell Height and Structural Performance
Geocell height plays a crucial role in load distribution. Taller cells provide higher vertical stiffness and better load transfer, particularly for heavy traffic applications. In addition, increased height allows for greater infill depth, which enhances compaction and reduces settlement. International buyers should consider height options ranging from 50mm to 200mm based on intended project applications.
Combined Effects on Constraint Efficiency
Optimizing both grid size and height ensures maximum geocell performance. Proper combinations of these parameters enhance soil confinement, reduce lateral movement, and improve overall stability. Manufacturers often perform laboratory tests, including plate load and shear tests, to validate performance under specific grid configurations.
Manufacturing and Application Process
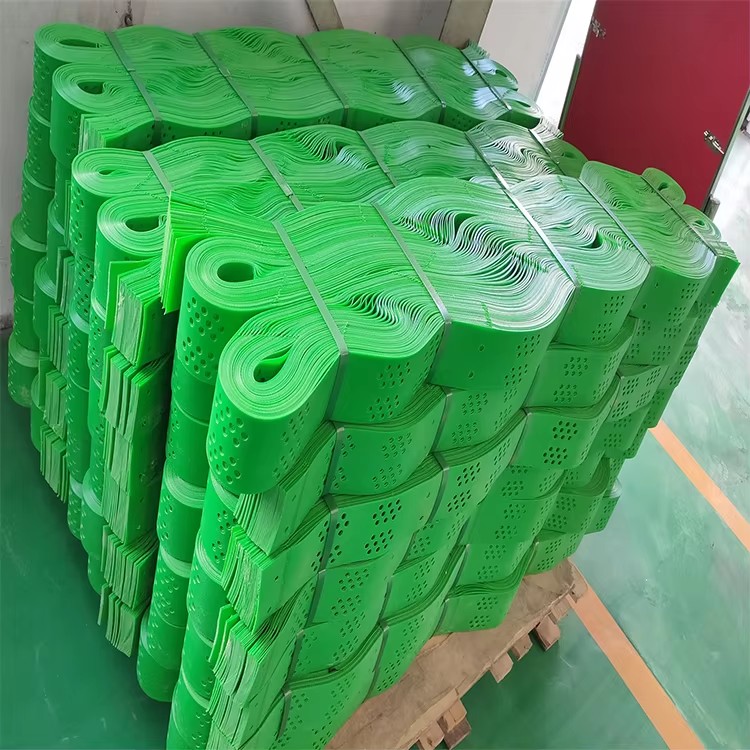
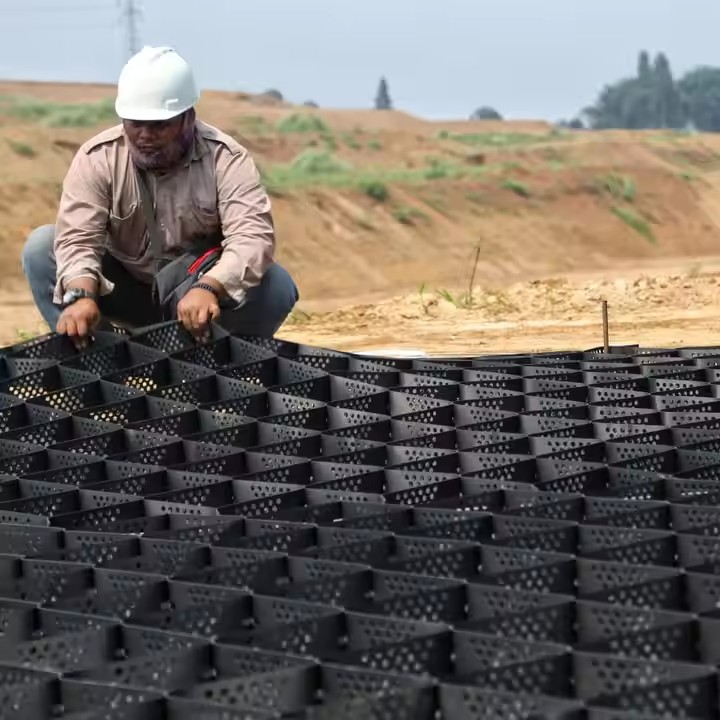
High-quality geocells are typically manufactured from high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE) using extrusion and welding processes. Each cell is connected to form a modular 3D grid, allowing for easy deployment on-site. Installation involves laying geocells over prepared subgrades, filling them with soil, sand, or aggregate, and compacting the infill to achieve optimal confinement.
International buyers should ensure that the geocell supplier provides consistent quality, UV-stabilized material, and customizable grid dimensions to suit diverse engineering requirements.
Trends and Considerations for International Buyers
Sustainability and cost-efficiency are emerging trends in geocell applications. Recycled HDPE geocells offer environmental benefits while maintaining structural integrity. Additionally, modular designs and pre-assembled panels reduce installation time and labor costs.
Buyers should consider:
Environmental impact of raw materials.
Load-bearing requirements for specific projects.
Flexibility of grid size and height to match engineering needs.
Supplier compliance with international quality standards.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How do grid size and height affect geocell performance?
Smaller grid sizes enhance lateral soil confinement, while taller cells improve vertical stiffness and load distribution. The combination of optimized height and grid size ensures maximum constraint efficiency.
2. What types of infill materials can be used in geocells?
Geocells can be filled with sand, gravel, soil, or recycled materials depending on project requirements. Proper compaction of infill ensures optimal stability and load-bearing performance.
3. Are HDPE and LLDPE geocells suitable for extreme weather conditions?
Yes, UV-stabilized HDPE and LLDPE geocells are resistant to temperature variations, moisture, and chemical exposure, making them suitable for diverse climates.
4. Can geocells be customized for large-scale infrastructure projects?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customizable grid sizes, heights, and panel dimensions to meet specific project requirements, ensuring efficient installation and optimal performance.
Conclusion and Call to Action
For international B2B buyers seeking reliable 3D grid geocells with high constraint efficiency, understanding the relationship between grid size, height, and soil performance is critical. We provide high-quality geocells with customizable dimensions, UV stabilization, and durable materials designed to meet global engineering standards. Contact us today to discuss bulk orders and secure optimized solutions for your next infrastructure or erosion control project.