High Density Polyethylene Geomembrane
Manufacturing Process
The production of High Density Polyethylene Geomembrane follows standardized industrial procedures:
Raw Material Selection: Virgin or controlled recycled HDPE resin
Compounding: Blending with carbon black and stabilizers
Extrusion: Flat-die or blown film extrusion forming continuous sheets
Surface Texturing: Optional embossing for increased interface friction
Cooling and Thickness Control: Ensures uniformity
Online Quality Monitoring: Thickness and defect detection
Mechanical Testing: Tensile, tear, puncture, and OIT verification
Rolling and Packaging: Controlled winding for transport safety
Product Definition
High Density Polyethylene Geomembrane is an impermeable synthetic liner manufactured from high-density polyethylene resin, engineered to provide long-term containment, waterproofing, and environmental protection in civil, mining, hydraulic, and infrastructure engineering projects.
Technical Parameters and Specifications
Typical engineering-grade High Density Polyethylene Geomembrane parameters used in design and procurement include:
Material: High-density polyethylene (HDPE)
Density: ≥ 0.94 g/cm³
Thickness Range: 0.5 mm – 3.0 mm
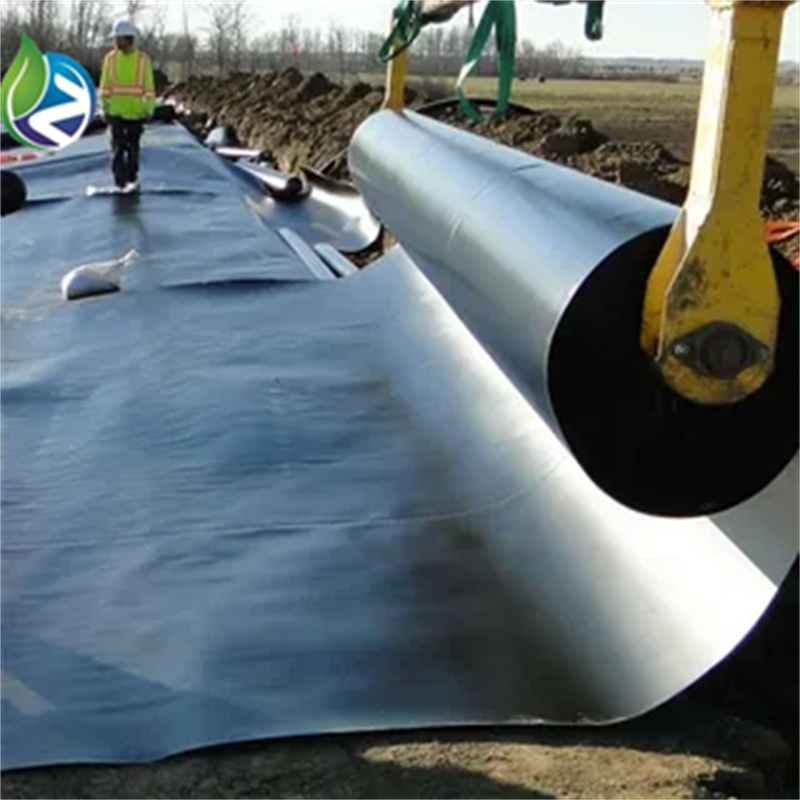
Standard Roll Width: 5.0 m – 8.0 m
Roll Length: 50 m – 200 m
Tensile Strength at Yield: ≥ 15 MPa
Elongation at Break: ≥ 700%
Puncture Resistance: ≥ 300 N
Carbon Black Content: 2.0% – 3.0%
Oxidative Induction Time (OIT): ≥ 100 minutes
Design Service Life: ≥ 50 years
Structure and Material Composition
High Density Polyethylene Geomembrane is a homogeneous polymer sheet designed for chemical and mechanical stability:
HDPE Polymer Matrix: Provides impermeability and tensile strength
Carbon Black: Enhances UV resistance and weather durability
Antioxidant System: Delays thermal and oxidative degradation
Surface Options: Smooth or textured for slope friction control
Manufacturing Process
The production of High Density Polyethylene Geomembrane follows standardized industrial procedures:
Raw Material Selection: Virgin or controlled recycled HDPE resin
Compounding: Blending with carbon black and stabilizers
Extrusion: Flat-die or blown film extrusion forming continuous sheets
Surface Texturing: Optional embossing for increased interface friction
Cooling and Thickness Control: Ensures uniformity
Online Quality Monitoring: Thickness and defect detection
Mechanical Testing: Tensile, tear, puncture, and OIT verification
Rolling and Packaging: Controlled winding for transport safety
Industry Comparison
| Material | Impermeability | Chemical Resistance | Durability | Relative Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High Density Polyethylene Geomembrane | Excellent | Excellent | Very High | Medium |
| LLDPE Geomembrane | Excellent | Good | High | Medium |
| PVC Liner | Good | Moderate | Moderate | Medium |
| EPDM Rubber | Excellent | Good | High | High |
Application Scenarios
High Density Polyethylene Geomembrane is widely specified by EPC contractors, consultants, and distributors for:
Municipal and hazardous waste landfill liners
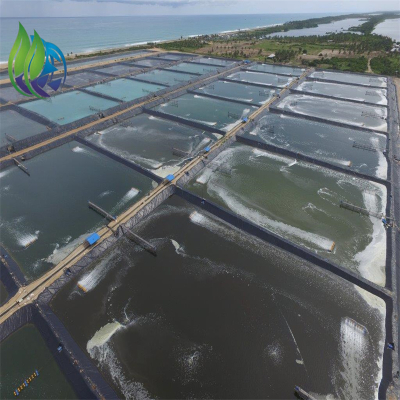
Mining tailings storage facilities and heap leach pads
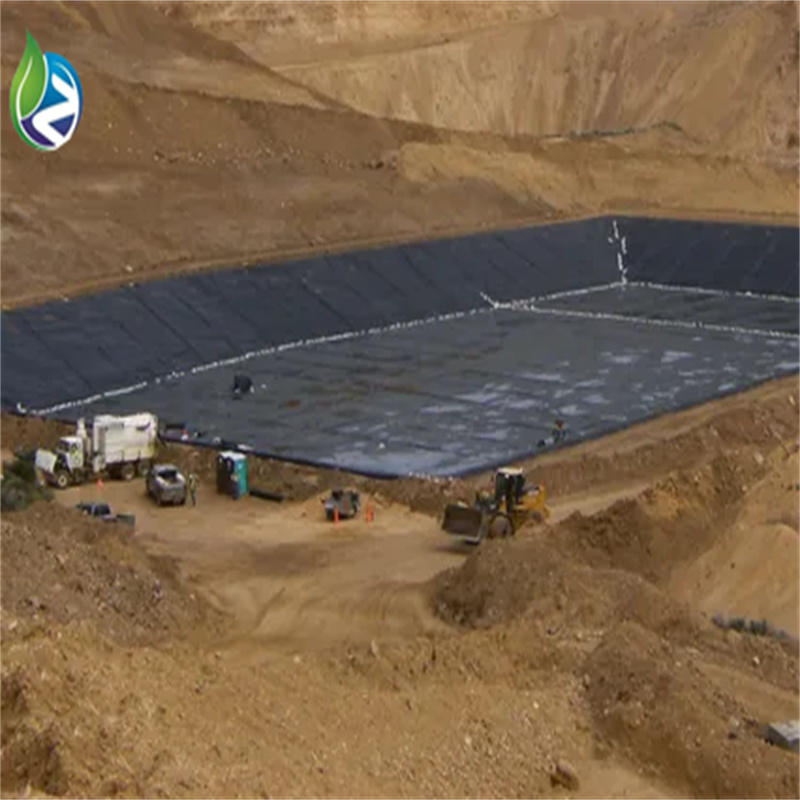
Industrial wastewater treatment ponds
Reservoirs, canals, and irrigation systems
Aquaculture ponds and water storage lagoons
Secondary containment for chemical storage
Core Pain Points and Engineering Solutions
Leakage Control: Near-zero permeability prevents fluid migration
Chemical Attack: HDPE resists acids, alkalis, and hydrocarbons
UV Degradation: Carbon black stabilization ensures long-term exposure resistance
Subgrade Movement: High elongation accommodates settlement and deformation
Risk Warnings and Mitigation Measures
Ensure subgrade is smooth and free of sharp objects
Use protective geotextile layers where puncture risk exists
Employ certified welding technicians for seam installation
Allow thermal expansion during high-temperature installation
Procurement and Selection Guide
Define containment function and regulatory requirements
Select thickness based on hydraulic head and loading
Determine surface texture requirements for slopes
Verify compliance with ASTM and ISO standards
Review manufacturer quality control documentation
Confirm availability of installation and seam testing support
Engineering Case Study
A mining tailings pond project adopted a 2.0 mm High Density Polyethylene Geomembrane installed over a compacted subgrade with needle-punched geotextile protection. Hot wedge welding with dual seams and air pressure testing ensured seam integrity. After multiple operational cycles, monitoring confirmed zero leakage.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What makes HDPE geomembrane impermeable?
A: Its dense polymer structure provides near-zero permeability.Q2: What thickness is most common?
A: 1.0–2.0 mm for most containment projects.Q3: Is it suitable for chemical exposure?
A: Yes, HDPE has excellent chemical resistance.Q4: Can it be used in exposed conditions?
A: Yes, UV stabilization allows long-term exposure.Q5: How are seams joined?
A: By hot wedge or extrusion welding.Q6: Is textured geomembrane necessary on slopes?
A: Recommended where slope stability is critical.Q7: What standards apply?
A: ASTM D638, D6693, D5885, ISO equivalents.Q8: Can damaged areas be repaired?
A: Yes, with localized patch welding.Q9: How long does it last?
A: Over 50 years under standard service conditions.Q10: Is geotextile always required?
A: Recommended where puncture risk exists.
Call to Action
For technical datasheets, project-specific quotations, or High Density Polyethylene Geomembrane samples, submit your engineering requirements to receive professional procurement and technical support.
E-E-A-T Author Credentials
This content is prepared by professionals with extensive experience in geosynthetics engineering, containment system design, and infrastructure project support, serving EPC contractors, consultants, and international procurement teams.