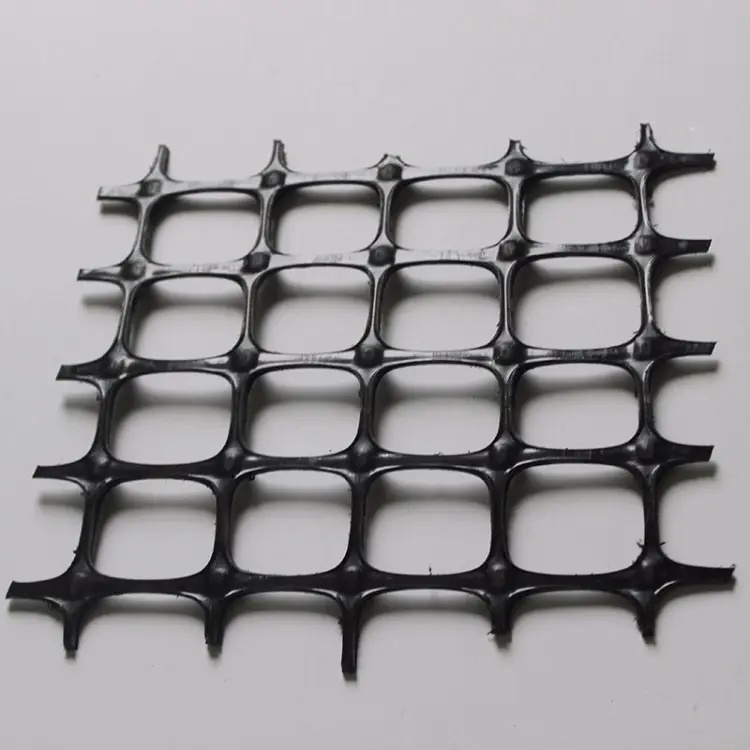
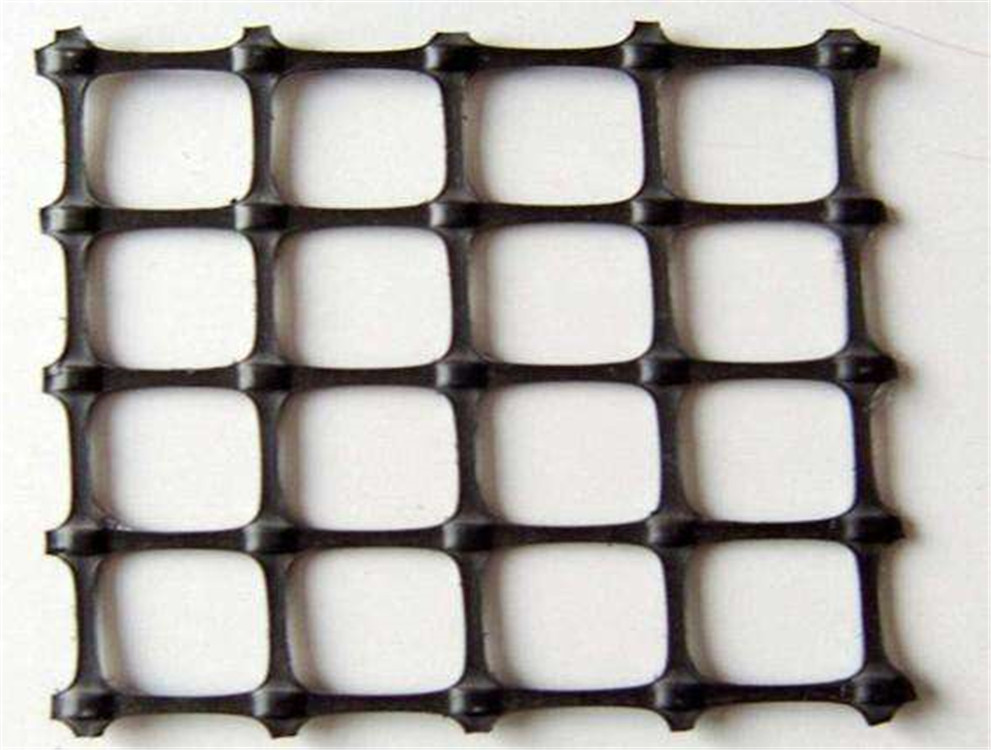
Hdpe Uniaxial Geogrid
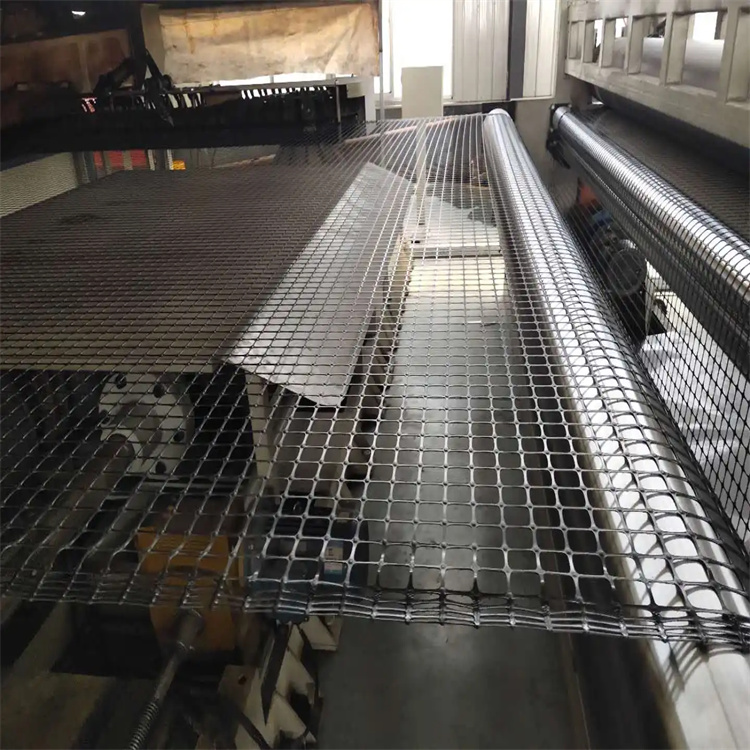
The plastic geogrid is formed by stretching a square or rectangular polymer mesh material, which can be one-way stretching and bidirectional stretching according to the different drawing directions when it is manufactured. It is made by punching holes in an extruded polymer sheet (mostly polypropylene or high-density polyethylene), and then subjected to directional stretching under heating conditions.
Support bulk ordering with favorable prices.
Support ODM/OEM.
The factory has stock and fast delivery.
Delivery Time: 10-20 working days
Minimum Order Quantity: 300 square meters
Payment Term: 30% T/T Deposit, 70% T/T Before Shipping
When it comes to infrastructure that lasts, the quality of the roadbed reinforcement makes all the difference. Enter HDPE Geogrid Roadbed Reinforcement—a revolutionary material engineered to provide superior load distribution, enhanced stability, and extended lifespan for road construction projects.
If you’re working in road engineering, municipal development, or heavy transportation infrastructure, it’s time to take a serious look at what HDPE geogrid roadbed reinforcement can offer.
What Is HDPE Geogrid Roadbed Reinforcement?
HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) geogrid roadbed reinforcement is a polymer-based, grid-like synthetic material used under roads, railways, and foundations to improve soil structure and load-bearing performance. Its interlocking structure distributes weight efficiently and prevents rutting, cracking, and displacement of aggregates over time.
Why Use HDPE Geogrid for Roadbed Reinforcement?
Let’s dive into the core benefits of HDPE geogrid in road construction:
1. Exceptional Tensile Strength
HDPE geogrids are engineered to withstand extreme tension, making them ideal for high-load zones like highways, industrial parks, and heavy-haul corridors.
? “We noticed a massive reduction in surface deformation after switching to HDPE geogrid roadbed reinforcement. Definitely worth the investment.”
— @InfraBuildTech, Site Engineer
2. Improved Load Distribution
By evenly dispersing pressure across a broader area, HDPE geogrids reduce the risk of roadbed failure, even under frequent and heavy traffic.
3. Enhanced Soil Interaction
The interlocking grid pattern of HDPE geogrids creates mechanical stability with surrounding aggregates, reducing subgrade strain and increasing overall stiffness.
4. Long-Term Cost Efficiency
Using HDPE geogrid roadbed reinforcement lowers maintenance costs by improving durability and reducing the need for frequent resurfacing.
? “In rural roads especially, HDPE geogrid has drastically cut back repair costs. It’s a game-changer for small budgets.”
— @RuralRoadSolutions
Where Is HDPE Geogrid Roadbed Reinforcement Used?
This versatile material has become the go-to solution in various civil engineering applications:
Highways and expressways
Access roads to industrial sites
Railway embankments
Parking lots and container terminals
Slope stabilization and retaining walls
In each case, HDPE geogrid roadbed reinforcement helps ensure long-term performance, even in challenging soil or climate conditions.
Installation Made Simple
One of the top reasons engineers prefer HDPE geogrid is its ease of deployment:
Site Preparation: Clear and level the base soil.
Roll Out the Geogrid: Place the HDPE geogrid flat over the surface.
Overlap Edges: Ensure proper overlapping (typically 20–30 cm) between rolls.
Secure with Pins or Staples: Anchor the material firmly in place.
Backfill with Aggregates: Add and compact granular material on top.
This streamlined installation saves time, labor, and costs—especially on large-scale projects.
Choosing the Right HDPE Geogrid
When selecting HDPE geogrid roadbed reinforcement, consider:
Grid aperture size (dependent on aggregate type)
Tensile strength rating
UV and chemical resistance
Biaxial vs. uniaxial performance
? “We chose a biaxial HDPE geogrid for our port project, and it exceeded expectations for load handling.”
— @GlobalPortsInfra
User Feedback: Real Projects, Real Results
⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️
“Reliable under pressure”
“We’ve been using HDPE geogrid roadbed reinforcement in all our regional roads. The ground stability improvement is noticeable even months after.”
— @CityConstructSolutions
⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️
“Easy to install, excellent ROI”
“Installation was quicker than we anticipated, and the cost savings over traditional methods are obvious.”
— @QuickBuildPavements
⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️
“Built to last”
“We used HDPE geogrids on a freight road with constant truck traffic. After two years, no rutting or cracking. Impressive performance.”
— @LogiTrackInfra
Final Thoughts: Reinforce With Confidence
For any roadwork, foundation, or infrastructure project that demands strength, longevity, and smart engineering, HDPE geogrid roadbed reinforcement is the smart choice. It’s not just about building roads—it’s about building them to last.
If you're an engineer, contractor, or project manager seeking a proven solution to subgrade stabilization, investing in HDPE geogrid roadbed reinforcement is a decision you won’t regret.
The role of the geogrid mainly includes the following aspects:
Geogrids are essential components in geotechnical and civil engineering, providing reinforcement and stability to soil structures. These high-strength, polymer-based grids are widely used in infrastructure projects such as roads, railways, retaining walls, and embankments. Their primary function is to enhance soil performance by improving load distribution, preventing deformation, and extending the lifespan of structures.
Functions of Geogrids
1. Soil Reinforcement
Geogrids provide tensile strength to weak soils, enhancing their load-bearing capacity. By interlocking with soil particles, geogrids distribute loads more evenly, reducing stress concentration and preventing subsidence or failure in embankments and foundations.
2. Erosion Control
In areas prone to erosion, geogrids help stabilize slopes and prevent soil displacement. They are commonly used in combination with vegetation or geotextiles to mitigate the effects of wind and water erosion, ensuring long-term stability of slopes and embankments.
3. Pavement Improvement
In road and railway construction, geogrids increase pavement durability by reducing rutting and cracking. By reinforcing base and subgrade layers, they enhance the structural integrity of transportation networks, minimizing maintenance costs and extending service life.
4. Retaining Wall Stability
Geogrids are integral to reinforced retaining walls, enabling the construction of steep slopes without excessive material use. They improve wall stability by distributing lateral forces, reducing the risk of structural failure, and allowing for more cost-effective designs.
Advantages of Geogrids
Enhanced Load Distribution: Prevents uneven settlement and improves foundation performance.
Cost-Effectiveness: Reduces the need for expensive excavation and soil replacement.
Eco-Friendly: Minimizes environmental impact by optimizing material usage and reducing erosion.
Long-Term Durability: Resistant to chemical degradation, UV exposure, and biological decay.