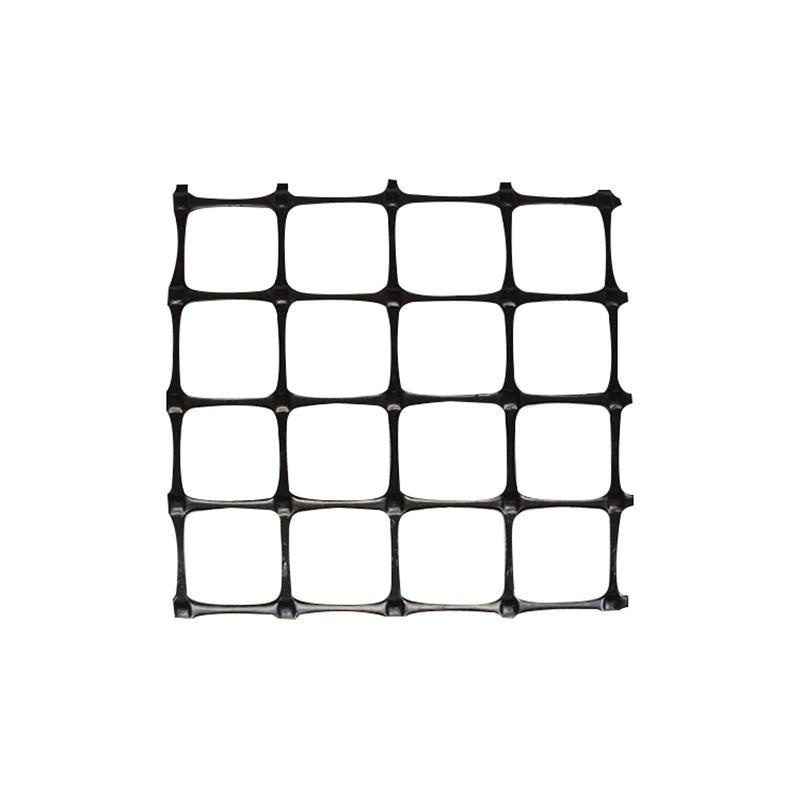
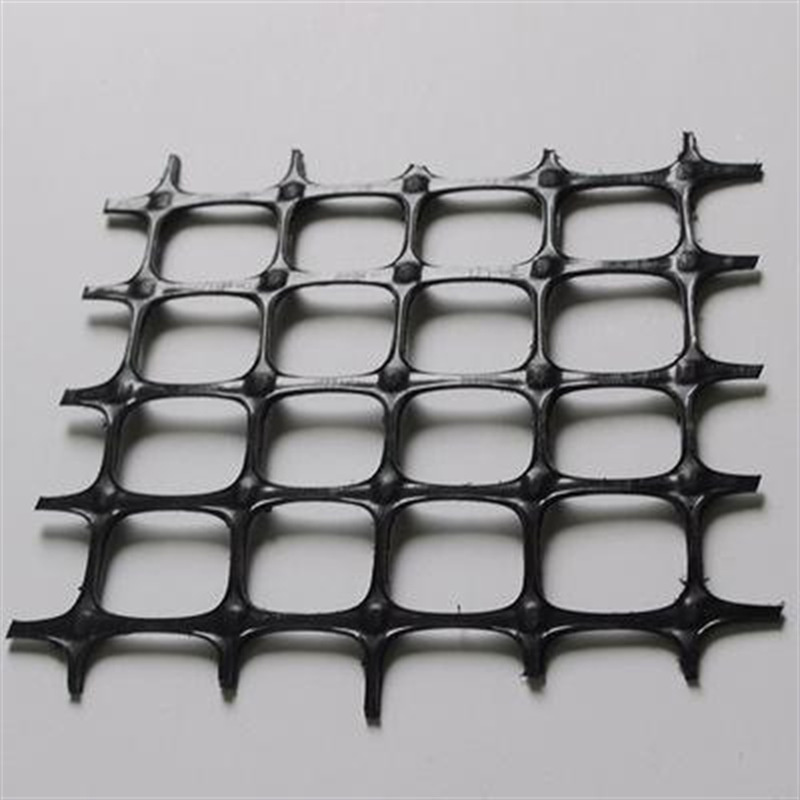
Biaxial Geogrid Price
Biaxial stretch plastic geogrid is made of high polymer by extrusion. The board is formed. The punching process is followed by longitudinal and transverse stretching. The material has great tensile strength both longitudinally and transversely. This structure could also provide an ideal interlocking system to more efficiently withstand and diffuse forces in the soil. It is suitable for reinforcement of large area permanent load.
Support bulk ordering with favorable prices.
Support ODM/OEM.
The factory has stock and fast delivery.
Delivery Time: 10-20 working days
Minimum Order Quantity: 300 square meters
Payment Term: 30% T/T Deposit, 70% T/T Before Shipping
When it comes to ensuring the long-term durability and stability of any civil engineering project, Biaxial Geogrids for Foundation Reinforcement are a game-changing solution. These high-performance geosynthetics are engineered to strengthen weak soils, distribute loads evenly, and significantly reduce settlement—making them ideal for roads, buildings, retaining walls, and more.
In this comprehensive guide, we explore how Biaxial Geogrids for Foundation Reinforcement work, their benefits, applications, and how to choose the right type for your next project.
What Are Biaxial Geogrids?
Biaxial Geogrids are synthetic mesh-like materials made primarily from high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or polypropylene (PP). Unlike uniaxial geogrids that offer strength in one direction, biaxial geogrids provide equal strength in both the longitudinal and transverse directions. This unique feature makes them ideal for applications requiring multi-directional load distribution, especially in foundation reinforcement.
When used as part of a subgrade stabilization or base reinforcement system, Biaxial Geogrids for Foundation Reinforcement improve load-bearing capacity, prevent rutting, and minimize deformation over time.
Key Benefits of Biaxial Geogrids for Foundation Reinforcement
✅ Superior Load Distribution
The interlocking structure of biaxial geogrids helps distribute heavy loads across a wider area, reducing pressure on weak soils and extending the life of the foundation.
✅ Increased Bearing Capacity
By reinforcing the sub-base, Biaxial Geogrids for Foundation Reinforcement can significantly improve the load-bearing strength of unprepared or unstable soils.
✅ Reduced Soil Movement
These geogrids help prevent lateral soil displacement, which is critical in earthquake-prone zones and areas with variable soil conditions.
✅ Cost-Effective Construction
Using biaxial geogrids can reduce the need for expensive fill materials and cut down construction time—saving both labor and materials costs.
✅ Long-Term Durability
With excellent chemical resistance and UV stability, Biaxial Geogrids for Foundation Reinforcement perform reliably in a wide range of environmental conditions.
Applications of Biaxial Geogrids for Foundation Reinforcement
Thanks to their versatility and strength, biaxial geogrids are used in various infrastructure and construction projects, including:
Roads and Highways: Base course reinforcement and subgrade stabilization
Railways: Trackbed stabilization and load transfer improvement
Industrial Yards and Ports: Resistance to heavy static and dynamic loads
Foundations for Buildings: Prevent settlement and structural cracks
Parking Lots and Driveways: Reduce surface rutting and deformation
Airport Runways and Taxiways: Enhanced load distribution for aircraft
Whether for temporary access roads or permanent structural foundations, Biaxial Geogrids for Foundation Reinforcement deliver reliable, long-term performance.
How to Select the Right Biaxial Geogrid
When choosing Biaxial Geogrids for Foundation Reinforcement, consider the following factors:
1. Tensile Strength and Stiffness
Look for products with high tensile strength (typically ≥ 15 kN/m) and minimal elongation for effective stabilization.
2. Aperture Size and Shape
Ensure the geogrid matches your fill material. Most foundation applications work best with square apertures that promote aggregate interlock.
3. Material Type
HDPE and PP geogrids offer excellent resistance to chemicals and environmental degradation.
4. Certifications and Compliance
Choose products that comply with ASTM, ISO, or EN standards for quality and performance.
5. Manufacturer Reputation
Working with a trusted supplier ensures consistent quality, technical support, and faster delivery.
Installation Tips for Optimal Performance
Prepare a clean, level subgrade.
Unroll the biaxial geogrid over the area without tension.
Overlap adjacent rolls (usually 30–50 cm) and secure with pins or staples.
Place fill material (aggregate or soil) directly over the geogrid.
Compact in layers to enhance geogrid-soil interaction.
Following correct installation procedures ensures the Biaxial Geogrids for Foundation Reinforcement deliver their full performance potential.
Conclusion: Reinforce with Confidence
Biaxial Geogrids for Foundation Reinforcement are an essential tool in modern geotechnical engineering. Their ability to improve structural integrity, reduce material costs, and enhance long-term performance makes them indispensable in both public and private infrastructure projects.
If you're looking to build stronger, safer, and more sustainable foundations, Biaxial Geogrids for Foundation Reinforcement are the smart investment. Choose high-quality geogrids from reliable manufacturers to ensure optimal results.
Product construction method:
Bidirectional geogrid construction method: dig the foundation bed. set sand cushion layer (height difference is not more than 10 cm). roll into a platform. lay the grid. the longitudinal axis should be consistent with the main force direction. the longitudinal lap 15 to 20 cm. the transverse 10 cm. the lap with plastic tape binding. and on the laid grid. every two meters with U-shaped nails fixed on the ground. The geo-grid should be backfilled in time. and the number of geo-grid layers laid depends on the technical requirements.
Scope of application:
Civil engineering:
Such as land consolidation. foundation treatment. etc.
Traffic engineering:
Such as road. railway subgrade enhancement. slope protection. and airport runway. apron foundation reinforcement.
Hydraulic engineering:
Such as river flood control. dam reinforcement. etc.
Environmental protection projects:
Such as mountain protection. landslide control. etc.
Other fields:
Such as animal husbandry network. cage fish network. etc.