HDPE Geomembrane: Product Advantages and Wide Applications in Engineering Projects
Product Definition
HDPE geomembrane is a high-performance impermeable synthetic liner manufactured from high density polyethylene resin. It is designed to provide long-term seepage control, chemical resistance, and structural reliability in civil, hydraulic, environmental, and industrial engineering projects.
Technical Parameters and Specifications
Engineering performance of HDPE geomembrane is defined by standardized physical, mechanical, and durability indicators suitable for large-scale infrastructure projects.
Raw material: High Density Polyethylene (HDPE)
Standard thickness: 0.5 mm – 3.0 mm
Sheet width: 4.0 m – 8.0 m
Density: ≥0.94 g/cm³
Tensile strength at yield: ≥15 MPa
Elongation at break: ≥700%
Puncture resistance: ≥480 N
Carbon black content: 2.0%–3.0%
Oxidative induction time (OIT): ≥100 min
Service temperature range: -40°C to +60°C
Expected service life: 30–50 years (proper installation)
Structure and Material Composition
HDPE geomembrane is a homogeneous polymer sheet engineered for impermeability and durability.
Primary polymer matrix: High purity HDPE resin
Carbon black additive: UV resistance and aging protection
Antioxidants: Thermal and oxidative stability
Processing stabilizers: Ensure uniform melt flow and thickness
Manufacturing Process
Engineering-Oriented Production Steps
Raw HDPE resin selection and formulation control
High-temperature extrusion using flat-die or blown film lines
Sheet forming with automatic thickness calibration
Surface texturing (optional) for friction enhancement
Cooling, trimming, and roll winding
Quality inspection and laboratory testing
Core equipment: Extrusion lines, thickness scanners, tensile testers, carbon black dispersion analyzers.
Key process controls: Thickness tolerance, surface uniformity, additive dispersion, and thermal stability.
Industry Comparison
| Material | Impermeability | Chemical Resistance | Installation Efficiency | Lifecycle Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HDPE Geomembrane | Very High | Excellent | High | Low |
| LDPE Geomembrane | High | Good | High | Medium |
| Clay Liner | Medium | Low | Low | High |
| Concrete Lining | Medium | Medium | Low | High |
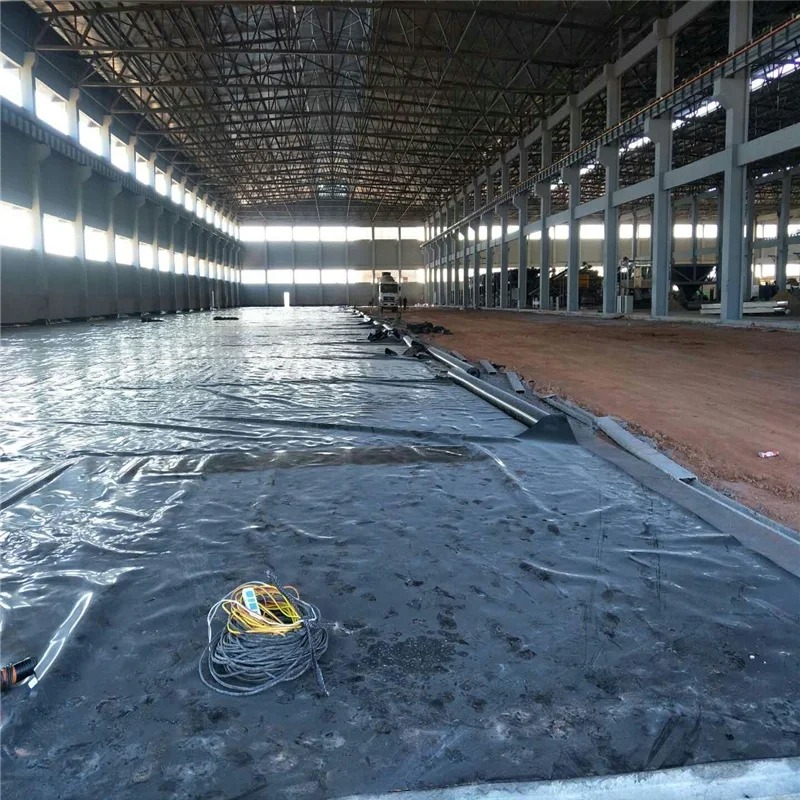
Wide Engineering Applications
HDPE geomembrane is widely applied across multiple engineering sectors due to its versatility and durability.
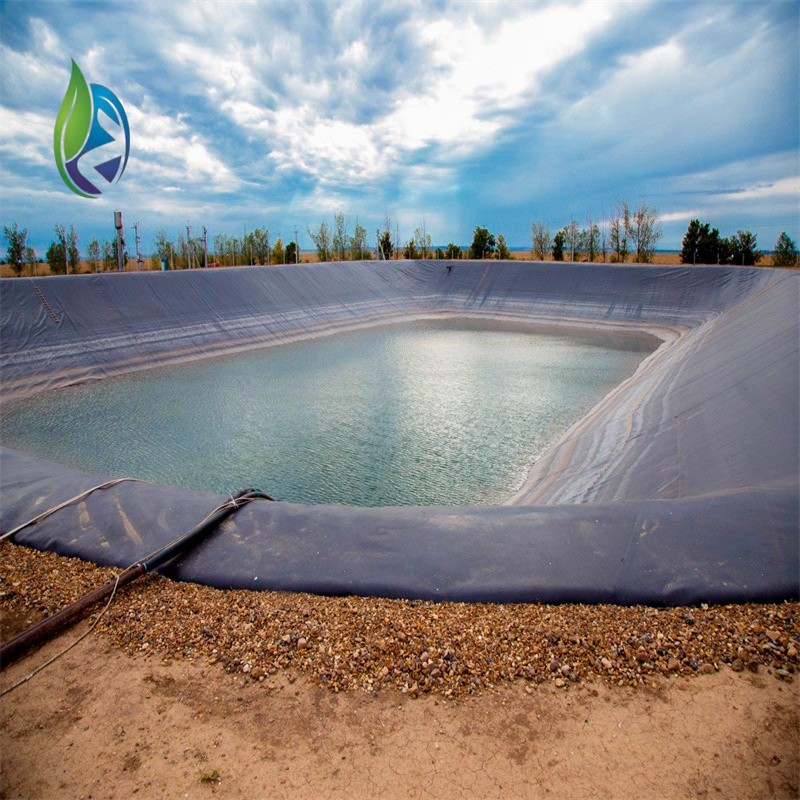
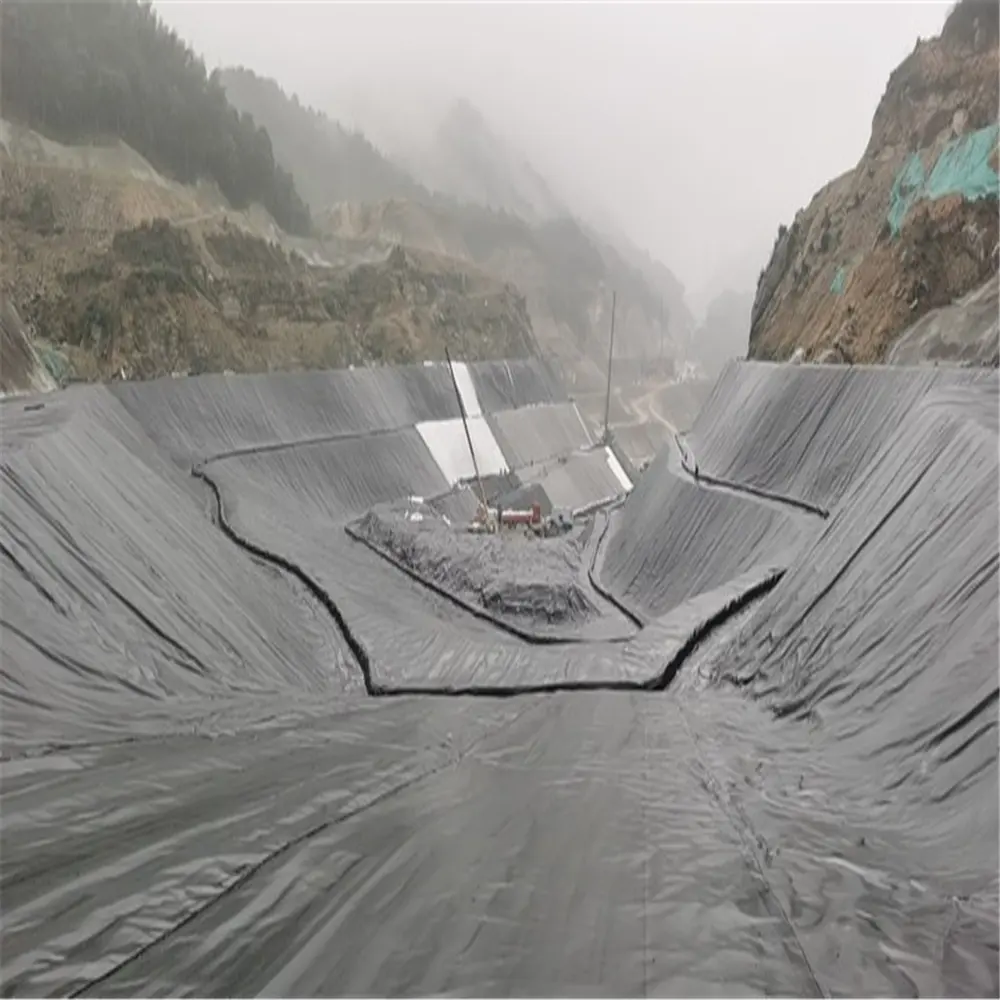
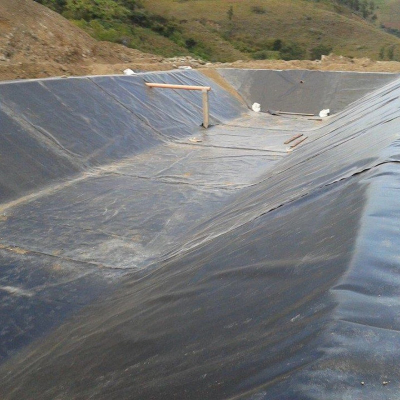
Water conservancy: Reservoirs, canals, dams, and irrigation systems
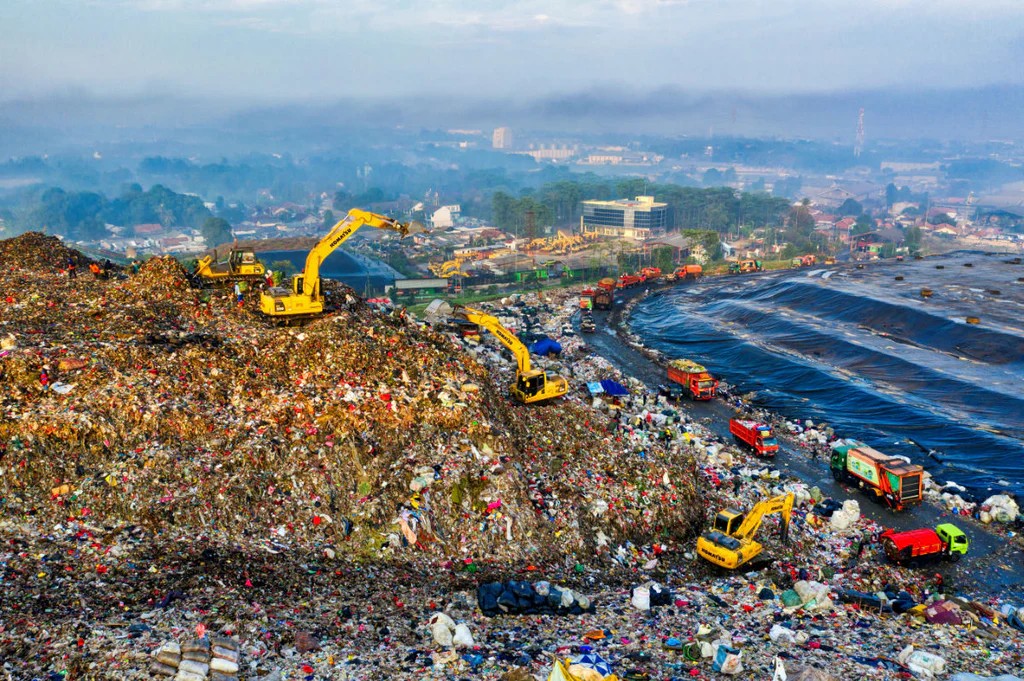
Environmental engineering: Landfills, leachate ponds, wastewater treatment
Mining projects: Heap leaching pads, tailings storage facilities
Aquaculture: Fish ponds and shrimp farming liners
Transportation: Tunnel waterproofing and subgrade protection
Core Pain Points and Engineering Solutions
Seepage losses: Continuous HDPE geomembrane provides near-zero permeability
Chemical corrosion: HDPE resists acids, alkalis, and salts
Structural deformation: High elongation accommodates settlement
Maintenance burden: Long service life reduces lifecycle maintenance costs
Risk Warnings and Mitigation Recommendations
Improper subgrade preparation can cause puncture risk
Unqualified welding may lead to leakage paths
Extended UV exposure before covering may accelerate aging
Inadequate anchoring can result in liner uplift
Procurement and Selection Guide
Define project application and hydraulic or environmental requirements
Select appropriate thickness based on pressure and load conditions
Determine smooth or textured surface requirements
Specify welding methods and seam testing standards
Verify compliance with ASTM, ISO, or EN standards
Evaluate supplier quality systems and project references
Plan logistics, installation schedule, and on-site handling
Engineering Case Example
In a municipal landfill expansion project, a 2.0 mm HDPE geomembrane was installed as the primary liner system over a compacted clay layer. The engineering plan included double-track hot wedge welding and 100% seam testing. Post-installation monitoring confirmed effective leachate containment and regulatory compliance.
FAQ
What is the main advantage of HDPE geomembrane? Excellent impermeability and durability.
Is HDPE geomembrane suitable for chemical exposure? Yes, it offers strong chemical resistance.
What thickness is commonly used? 1.0–2.0 mm for most engineering projects.
How are seams tested? Air pressure or vacuum box testing.
Can HDPE geomembrane handle settlement? Yes, due to high elongation.
Is UV resistance important? Yes, carbon black provides UV protection.
How long is the service life? Typically 30–50 years.
Can it be used underwater? Yes, for reservoirs and ponds.
Is third-party inspection recommended? Yes, for critical projects.
Does surface texture matter? Textured surfaces improve slope stability.
CTA
For project-specific HDPE geomembrane specifications, engineering drawings, pricing information, or material samples, please submit a formal request for quotation or technical documentation.
E-E-A-T Author Credentials
This article is prepared by a geosynthetics engineering specialist with over 15 years of experience in HDPE geomembrane design, manufacturing, and application across water conservancy, environmental protection, and mining infrastructure projects, supporting EPC contractors and global procurement teams.