Geocell for Slope Protection
Manufacturing Process
The production of Geocell for Slope Protection follows a standardized industrial workflow:
Resin Preparation: HDPE resin mixed with stabilizers and carbon black
Sheet Extrusion: Flat extrusion lines produce uniform HDPE sheets
Strip Cutting: Sheets cut into precise-width strips
Welding: Ultrasonic or hot welding forms cellular joints
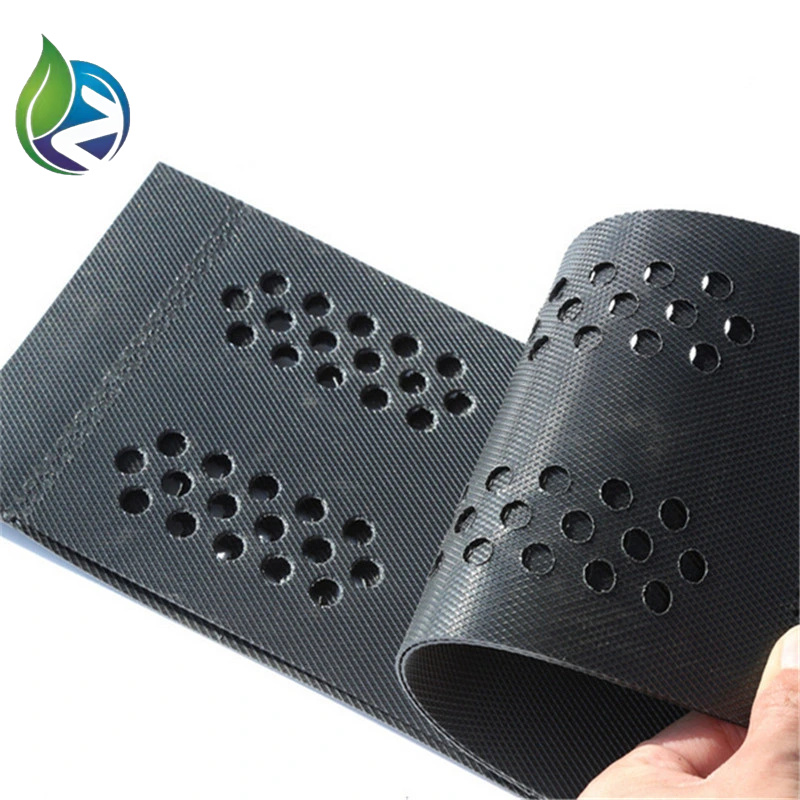
Perforation: Optional punching for drainage and root penetration
Expansion Testing: Verifies dimensional stability
Inspection and Packing: Mechanical tests and compact folding for transport
Product Definition
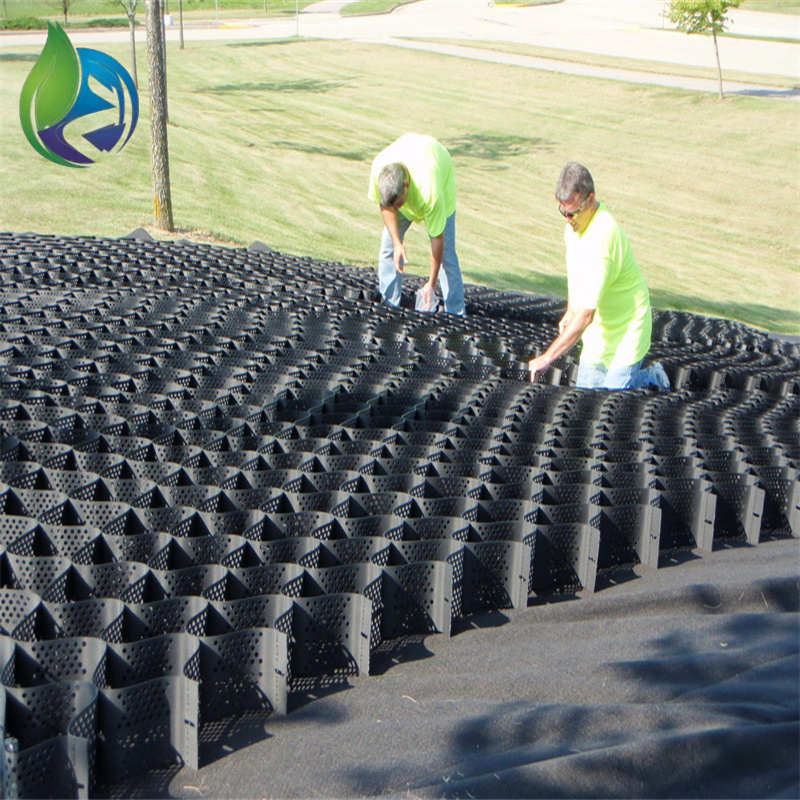
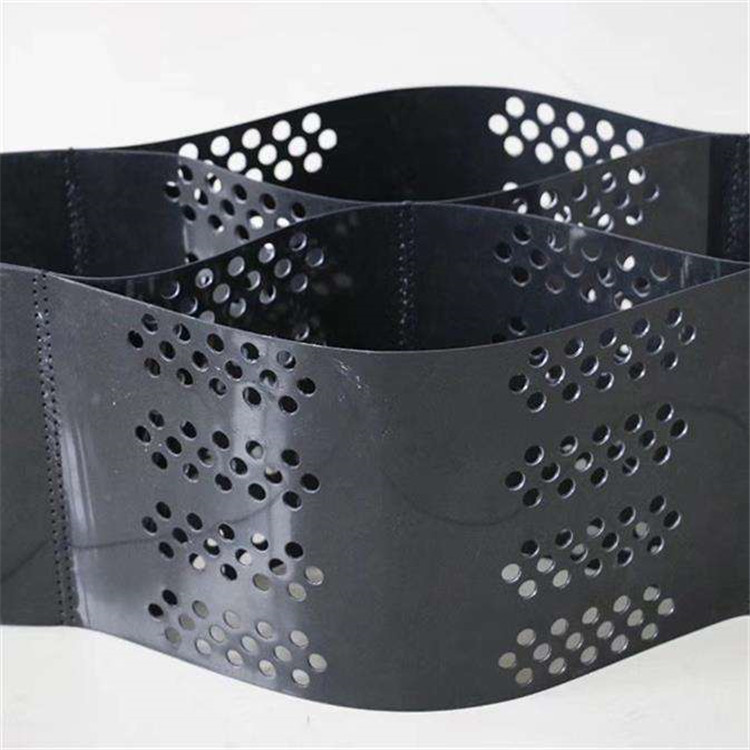
Geocell for Slope Protection is a three-dimensional cellular confinement system manufactured from high-density polyethylene, designed to stabilize slopes, prevent erosion, and improve load distribution by confining infill materials within interconnected cells under civil and geotechnical engineering conditions.
Technical Parameters and Specifications
The following parameters are commonly adopted in engineering design and procurement of Geocell for Slope Protection:
Raw Material: High-density polyethylene (HDPE)
Cell Height: 50 mm / 75 mm / 100 mm / 150 mm / 200 mm
Cell Size (Expanded): 210 × 210 mm or 250 × 250 mm
Sheet Thickness: 1.1 mm – 1.8 mm
Weld Peel Strength: ≥ 1000 N/100 mm
Tensile Strength: ≥ 20 MPa
Carbon Black Content: 1.5% – 2.5%
Operating Temperature: -40°C to +80°C
Design Service Life: ≥ 40 years under normal exposure
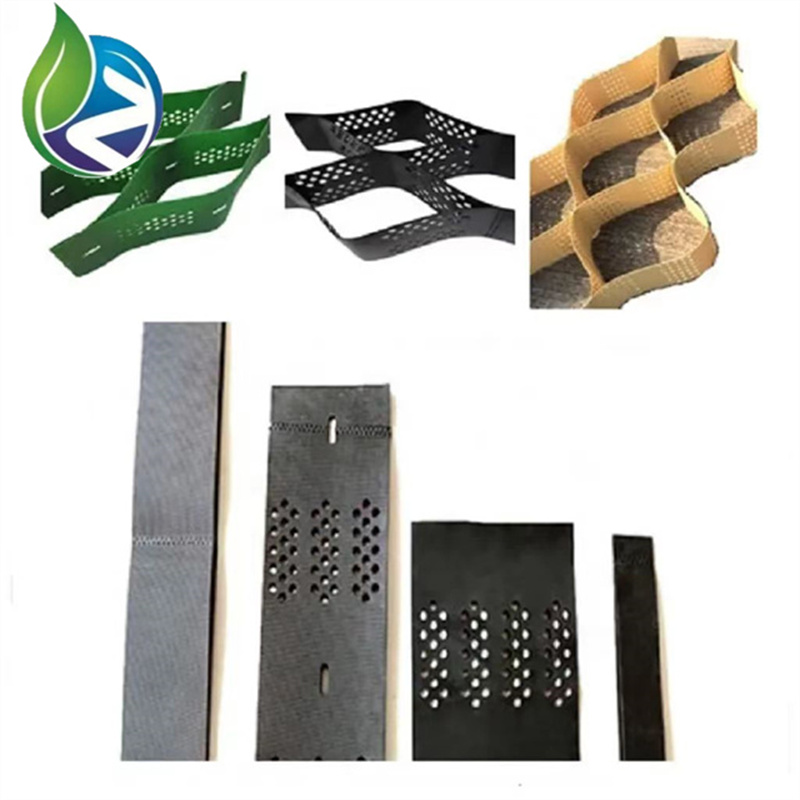
Structure and Material Composition
Geocell for Slope Protection adopts a honeycomb-like cellular structure formed by ultrasonic or thermal welding:
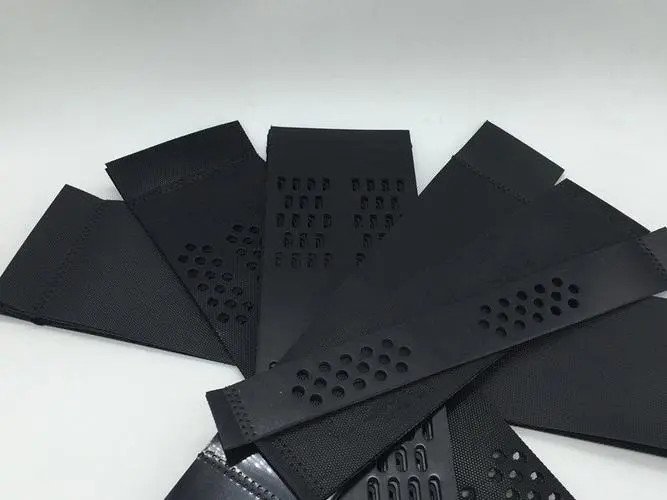
HDPE Strips: Provide flexibility, tensile strength, and chemical resistance
Welded Joints: Ensure structural integrity under shear and tensile stress
Perforated or Smooth Walls: Optional for drainage and vegetation integration
Three-Dimensional Cells: Confine soil, gravel, or concrete infill
Manufacturing Process
The production of Geocell for Slope Protection follows a standardized industrial workflow:
Resin Preparation: HDPE resin mixed with stabilizers and carbon black
Sheet Extrusion: Flat extrusion lines produce uniform HDPE sheets
Strip Cutting: Sheets cut into precise-width strips
Welding: Ultrasonic or hot welding forms cellular joints
Perforation: Optional punching for drainage and root penetration
Expansion Testing: Verifies dimensional stability
Inspection and Packing: Mechanical tests and compact folding for transport
Industry Comparison
| Solution Type | Erosion Control | Structural Reinforcement | Construction Speed | Lifecycle Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Geocell for Slope Protection | Excellent | High | Fast | Medium |
| Riprap Stone | Good | Medium | Slow | High |
| Concrete Slope Lining | Excellent | Very High | Medium | High |
| Vegetative Mat | Moderate | Low | Fast | Low |
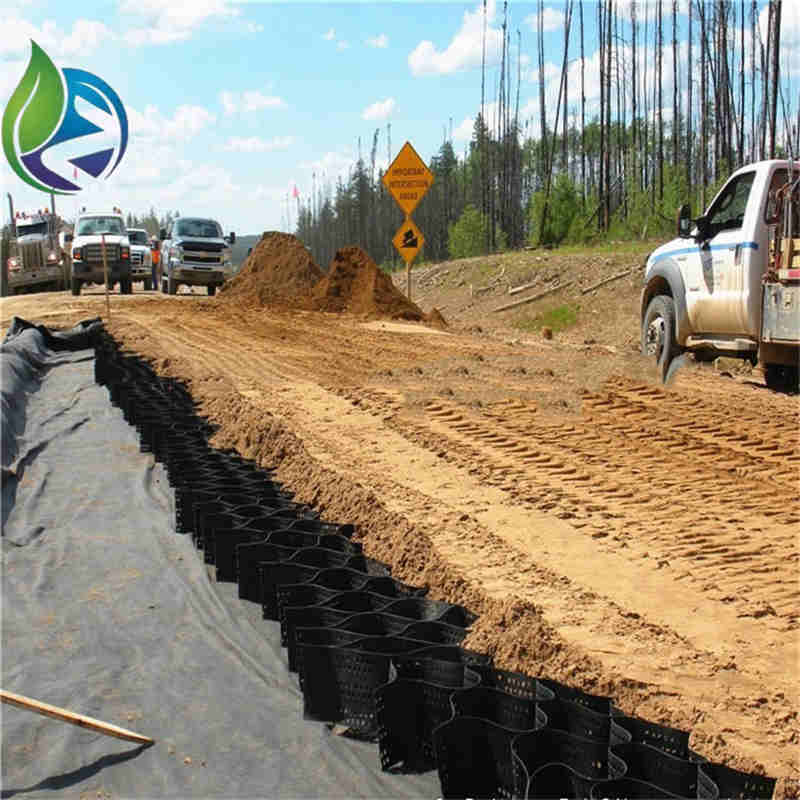
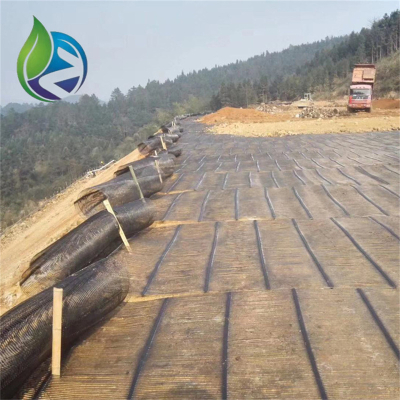
Application Scenarios
Geocell for Slope Protection is widely specified by EPC contractors, distributors, and engineering consultants for:
Highway and railway embankment slopes
Riverbank and canal slope stabilization
Landfill side slopes and capping systems
Mining waste dumps and haul road slopes
Retaining structure backslopes
Green slope protection with vegetation infill
Core Pain Points and Engineering Solutions
Slope Erosion: Cellular confinement reduces soil displacement under rainfall
Shear Failure: Improved load distribution limits downslope movement
Vegetation Loss: Cells protect root systems and retain moisture
High Maintenance Costs: Durable HDPE structure minimizes long-term repairs
Risk Warnings and Mitigation Measures
Ensure proper anchoring to prevent sliding on steep slopes
Avoid low-quality welds that reduce tensile performance
Select UV-stabilized material for exposed environments
Use appropriate infill material to match slope gradient
Procurement and Selection Guide
Define slope angle, height, and soil conditions
Select cell height based on erosion intensity
Determine perforated or non-perforated configuration
Verify mechanical and weld strength test reports
Confirm compatibility with infill material
Assess installation guidance and technical support availability
Engineering Case Study
In a highway expansion project, Geocell for Slope Protection with 150 mm cell height was installed on a 1:1.5 embankment slope. The cells were anchored at the crest, infilled with topsoil, and hydroseeded. After three monsoon seasons, no visible erosion or slope failure occurred, confirming long-term stability.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What slope angle is suitable?
A: Up to 70° with proper anchoring.Q2: Can geocells support vegetation?
A: Yes, with soil or sand infill.Q3: Are geocells UV resistant?
A: Yes, with carbon black stabilization.Q4: What infill materials are recommended?
A: Soil, gravel, or concrete.Q5: How are geocells installed?
A: Expanded, anchored, and infilled.Q6: Are geocells reusable?
A: Generally designed for permanent installation.Q7: Do perforations affect strength?
A: Slightly, but improve drainage.Q8: What standards apply?
A: ASTM, ISO, or project specifications.Q9: Can geocells be combined with geotextiles?
A: Yes, for filtration and separation.Q10: What is the typical service life?
A: Over 40 years.
Call to Action
For engineering quotations, technical datasheets, or slope protection project samples using Geocell for Slope Protection, please submit your project parameters to receive professional technical and procurement support.
E-E-A-T Author Credentials
This article is authored by geotechnical engineers with extensive experience in slope stabilization, erosion control systems, and geosynthetic applications for transportation, environmental, and infrastructure projects worldwide.