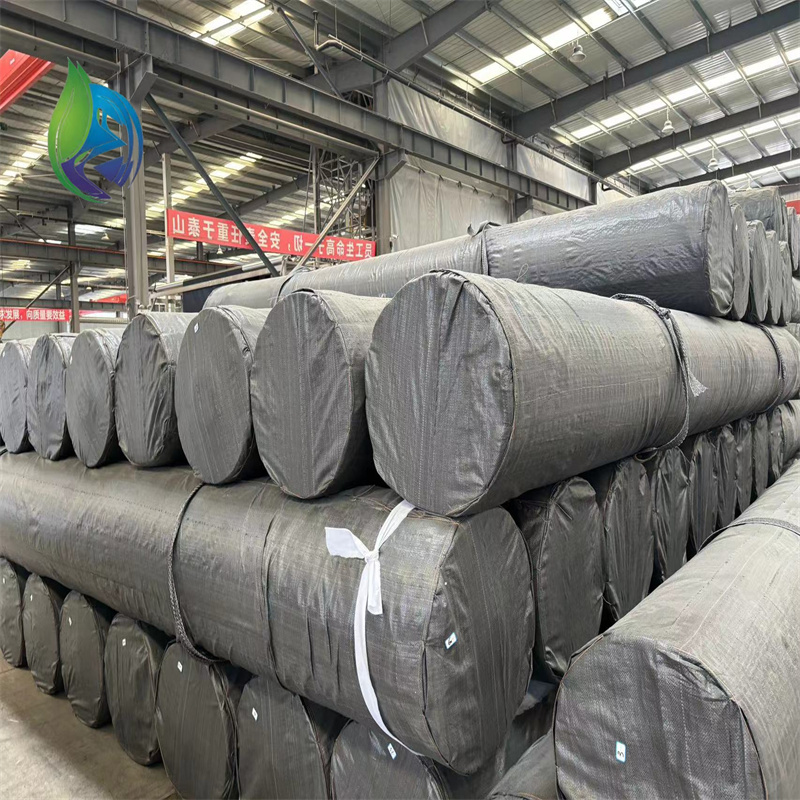
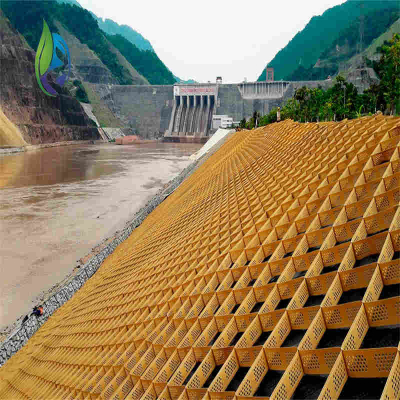
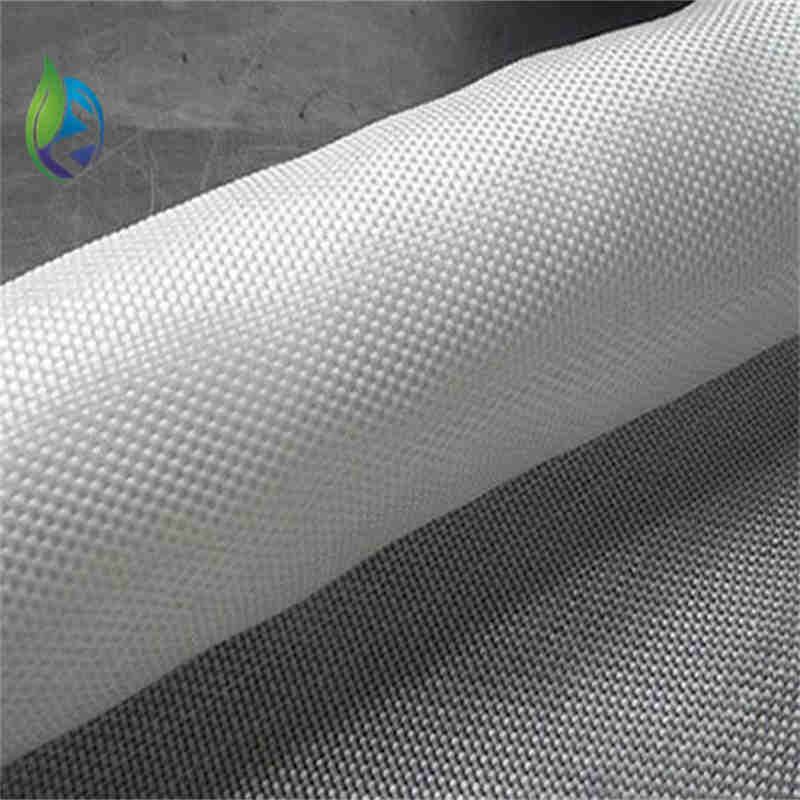
Filament Woven Geotextile
Manufacturing Process
Filament woven geotextile is produced using industrial textile manufacturing lines:
Polymer melting and filament extrusion
Filament drawing and orientation
Yarn winding and quality inspection
Warp and weft preparation
High-speed weaving on shuttle or rapier looms
Heat setting and dimensional stabilization
Surface inspection and mechanical testing
Roll cutting, labeling, and packaging
Product Definition
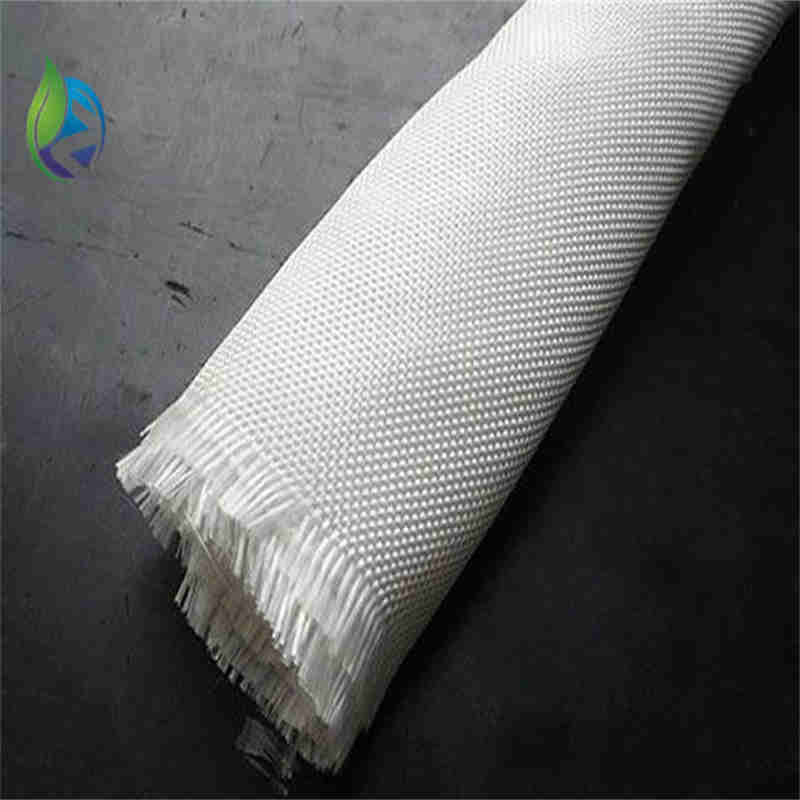
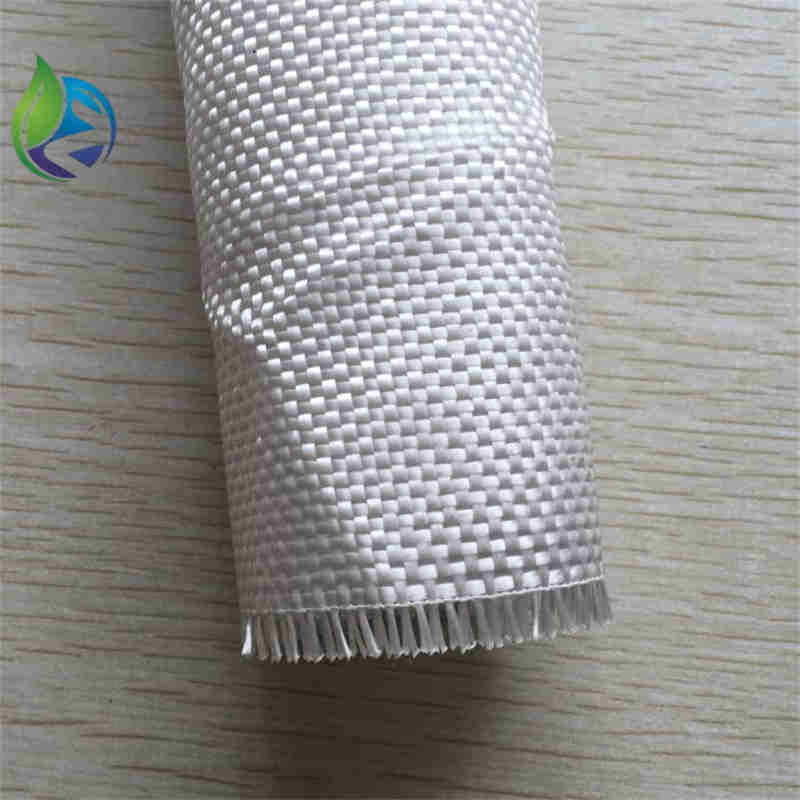
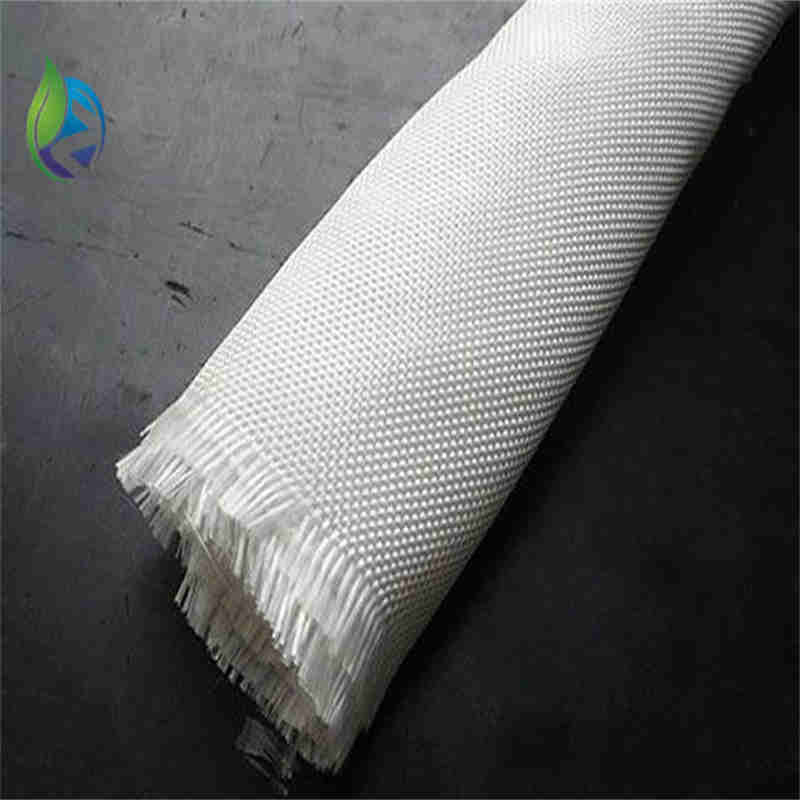
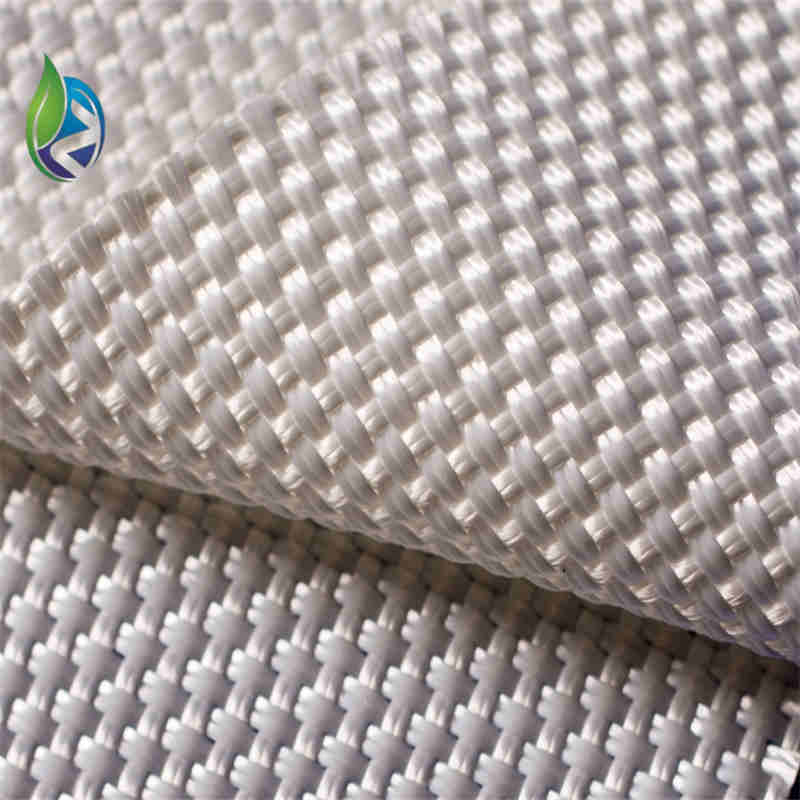
Filament woven geotextile is a high-strength geosynthetic manufactured from continuous polyester or polypropylene filaments woven into a stable fabric, designed to provide reinforcement, separation, and load distribution in civil and geotechnical engineering applications.
Technical Parameters and Specifications
Common engineering parameters for filament woven geotextile are as follows:
Raw material: Polyester (PET) or Polypropylene (PP)
Mass per unit area: 120 – 800 g/m²
Tensile strength (MD/XMD): 50 – 400 kN/m
Elongation at break: ≤ 15%
CBR puncture resistance: ≥ 6 – 20 kN
Equivalent opening size (O95): 0.05 – 0.40 mm
Permeability coefficient: ≥ 10⁻³ m/s
UV resistance: ≥ 70% retained strength after 500 hours
Design service life: ≥ 50 years (buried condition)
Structure and Material Composition
The performance of filament woven geotextile depends on its engineered textile structure:
Continuous Filament Yarns: Provide high tensile strength and low creep
Warp Direction (MD): Primary load-bearing axis
Weft Direction (XMD): Lateral stability and load distribution
Woven Interlacing: Controlled pore structure for filtration
Thermal or Chemical Stabilizers: Enhance durability and UV resistance
Manufacturing Process
Filament woven geotextile is produced using industrial textile manufacturing lines:
Polymer melting and filament extrusion
Filament drawing and orientation
Yarn winding and quality inspection
Warp and weft preparation
High-speed weaving on shuttle or rapier looms
Heat setting and dimensional stabilization
Surface inspection and mechanical testing
Roll cutting, labeling, and packaging
Industry Comparison
| Geotextile Type | Tensile Strength | Elongation | Filtration | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Filament Woven Geotextile | Very High | Low | Controlled | Reinforcement & Separation |
| Staple Fiber Nonwoven | Medium | High | Excellent | Filtration & Drainage |
| Slit-Film Woven | High | Low | Poor | Separation |
| Knitted Geotextile | Medium | Medium | Good | Specialized Reinforcement |
Application Scenarios
Filament woven geotextile is widely specified by EPC contractors and engineers for:
Road and highway base reinforcement
Railway subgrade stabilization
Embankment and slope reinforcement
Port, quay, and coastal engineering
Retaining walls and mechanically stabilized earth
Airport pavement structures
Core Pain Points and Solutions
Pain Point: Subgrade deformation under heavy load
Solution: High tensile strength filament woven geotextile reinforcementPain Point: Soil mixing between layers
Solution: Stable woven structure ensuring separationPain Point: Long-term creep failure
Solution: Continuous filament yarns with low creep characteristicsPain Point: Construction damage during installation
Solution: High puncture and tear resistance
Risk Warnings and Mitigation
Key risks associated with filament woven geotextile use include:
Improper orientation: always align MD with primary load direction
Insufficient overlap: maintain ≥ 300 mm overlaps or as designed
UV exposure during storage: cover rolls before installation
Incorrect pore size selection: match soil gradation requirements
Procurement and Selection Guide
Define project loading and design life
Select required tensile strength and elongation
Match filtration criteria to soil properties
Confirm compliance with project specifications
Review third-party laboratory test reports
Evaluate supplier manufacturing capacity
Assess logistics, roll size, and packaging
Engineering Case Study
In a highway widening project, filament woven geotextile with tensile strength of 200 kN/m was installed between weak subgrade and crushed stone base. Plate load tests showed bearing capacity improvement of over 40%, and post-construction settlement remained within design limits after five years of service.
FAQ
What is the main function? Reinforcement and separation.
Is it suitable for soft soil? Yes, with proper design.
How long is the service life? Over 50 years when buried.
Can it be used underwater? Yes, with appropriate material selection.
What is MD direction? Machine direction with higher tensile strength.
Does it allow drainage? Limited but controlled permeability.
Is it resistant to chemicals? Yes, to most soil chemicals.
Can it replace geogrids? In some reinforcement applications.
What roll sizes are available? Customized based on project needs.
Does it require skilled installation? Standard geotextile installation practices apply.
Call to Action
To request pricing, technical datasheets, design support, or engineering samples of filament woven geotextile, please submit your project specifications for professional evaluation.
E-E-A-T Author Statement
This article is prepared by geotechnical engineers and materials specialists with over 20 years of experience in geosynthetics design, testing, and large-scale infrastructure projects worldwide.