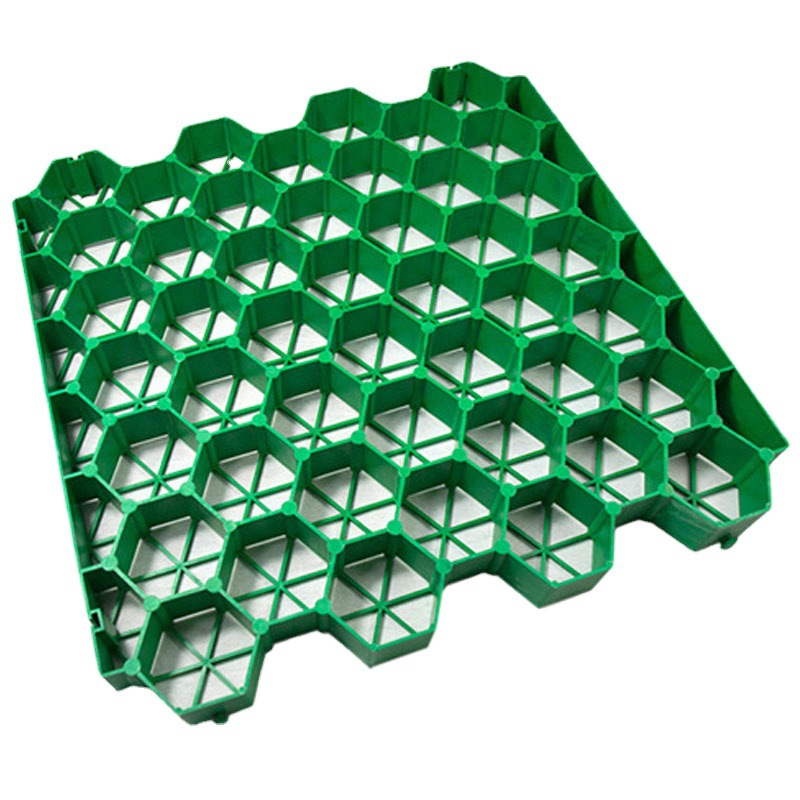
Grass Reinforcement Grids
Manufacturing Process
Raw Material Preparation: Virgin or recycled polymer pellet drying and filtration
Injection or Compression Molding: High-tonnage molding presses (800–1600 tons)
Cooling and Dimensional Stabilization: Controlled water and air cooling cycles
Edge Connector Forming: Precision forming of locking systems
Surface Texture Embossing: Mold-integrated surface roughness design
Quality Control: Load bearing, dimensional accuracy, and UV resistance testing
Packaging: Palletization and moisture-protected shrink wrapping
Product Definition
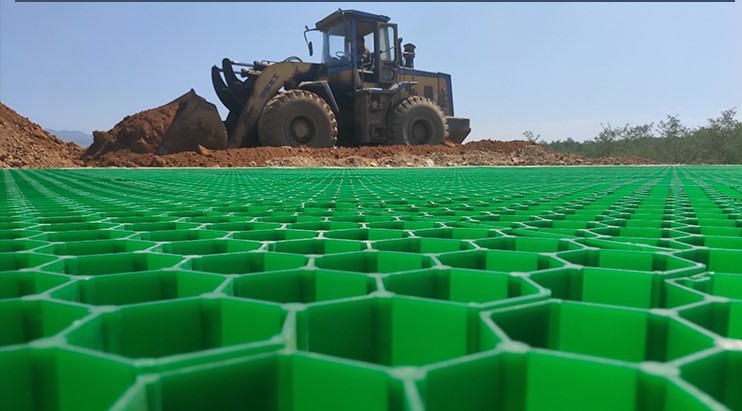
Grass Reinforcement Grids are load-bearing cellular pavement systems manufactured from polymer or concrete composites, designed to stabilize turf surfaces while distributing traffic loads, preventing soil compaction, and enabling sustainable permeable ground solutions for light to heavy vehicular use.
Technical Parameters and Specifications
Base Material: High Density Polyethylene (HDPE) or Recycled Polypropylene (PP)
Standard Panel Size: 500 mm × 500 mm
Cell Height: 30 mm, 40 mm, 50 mm
Wall Thickness: 3.5–5.0 mm
Compressive Strength: ≥ 160 kN/m² (filled condition)
Load Capacity: Up to 400 tons/m² (with concrete infill)
Open Area Ratio: 90–95% vegetation void space
Operating Temperature Range: –40°C to +80°C
UV Resistance: ≥ 3000 hours accelerated weathering
Permeability Rate: > 95% surface water infiltration
Structure and Material Composition
Top Load Distribution Ribs: Honeycomb cell framework
Interlocking Joints: Snap-fit or hook-lock edge connectors
Bottom Drainage Channels: Integrated water flow paths
Geotextile Layer (optional): Nonwoven separator underlayment
Surface Rib Texture: Anti-slip, root anchoring micro-texture
Manufacturing Process
Raw Material Preparation: Virgin or recycled polymer pellet drying and filtration
Injection or Compression Molding: High-tonnage molding presses (800–1600 tons)
Cooling and Dimensional Stabilization: Controlled water and air cooling cycles
Edge Connector Forming: Precision forming of locking systems
Surface Texture Embossing: Mold-integrated surface roughness design
Quality Control: Load bearing, dimensional accuracy, and UV resistance testing
Packaging: Palletization and moisture-protected shrink wrapping
Industry Comparison
| System Type | Load Bearing Capacity | Drainage Performance | Installation Speed | Maintenance Requirement |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grass Reinforcement Grids | High | Excellent | Fast | Low |
| Concrete Pavers | Very High | Low–Medium | Medium | Medium |
| Gravel Systems | Low–Medium | High | Fast | High |
Application Scenarios
Emergency vehicle access routes
Parking lawns and overflow parking zones
Golf cart paths and resort landscaping
Fire lanes in commercial and residential developments
Slope stabilization and erosion control systems
Core Pain Points and Engineering Solutions
Soil Rutting Under Traffic: Cellular structure disperses wheel loads evenly
Poor Drainage and Waterlogging: High void ratio enables rapid infiltration
Vegetation Damage: Protective grid walls shield root zone from shear forces
Ground Settlement: Grid-reinforced layers reduce long-term deformation
Risk Warnings and Mitigation Recommendations
Risk: Inadequate subbase compaction
Mitigation: Minimum 95% Proctor density before grid placementRisk: Grid uplift during freeze-thaw cycles
Mitigation: Use geotextile separation and proper drainage layersRisk: UV degradation in storage
Mitigation: Store under UV-protective covers before installationRisk: Vegetation failure
Mitigation: Select grass species compatible with traffic load and climate
Procurement and Selection Guide
Define traffic load class and axle load requirements
Assess subgrade CBR value and moisture conditions
Select cell height based on design load and soil bearing capacity
Verify polymer grade and UV stabilization package
Request compressive and creep resistance test reports
Confirm interlocking compatibility for large-scale installation
Evaluate packaging efficiency for logistics and site handling
Engineering Application Case
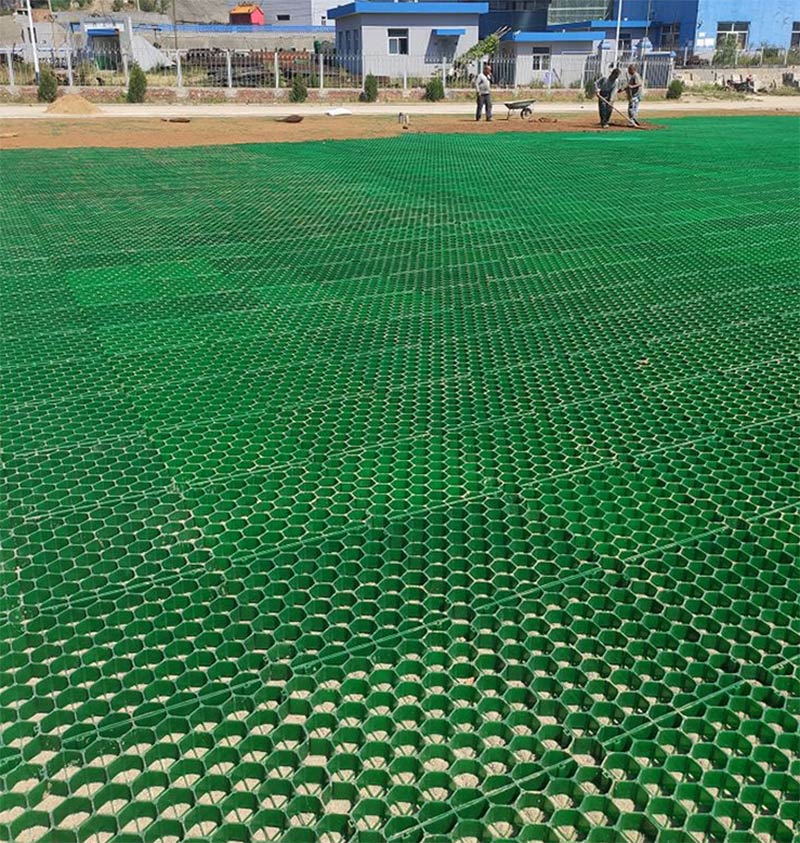
In a municipal overflow parking project of 9,500 m², Grass Reinforcement Grids with 40 mm cell height were installed over a compacted crushed stone base. The system was designed for occasional heavy truck access. Post-installation monitoring over two rainy seasons showed stable load performance and consistent turf coverage without visible rutting.
FAQ
Q1: Are Grass Reinforcement Grids suitable for heavy trucks? A: Yes, when designed with adequate base layers.
Q2: Can they be used in cold climates? A: Yes, tested for freeze-thaw resistance.
Q3: Do they require concrete infill? A: Not mandatory; soil and grass fill are common.
Q4: What is the typical service life? A: 20–25 years under proper installation.
Q5: Can grids be cut on site? A: Yes, with standard power tools.
Q6: Are they recyclable? A: Yes, for polymer-based products.
Q7: How fast can installation be completed? A: Typically 200–400 m² per crew per day.
Q8: Do they affect natural drainage? A: They improve surface infiltration.
Q9: Is weed control required? A: Standard landscaping maintenance applies.
Q10: Can they be used on sloped surfaces? A: Yes, with anchoring and geotextile support.
Call to Action
For project-based quotations, detailed technical datasheets, or engineering samples of Grass Reinforcement Grids, submit loading conditions, project dimensions, and environmental data to the technical sales department.
E-E-A-T Author Credentials
This technical article is authored by a senior geotechnical engineer with over 15 years of experience in permeable pavement systems, soil stabilization technologies, and large-scale civil infrastructure design and implementation.