3D Geomat for Erosion Control
Manufacturing Process
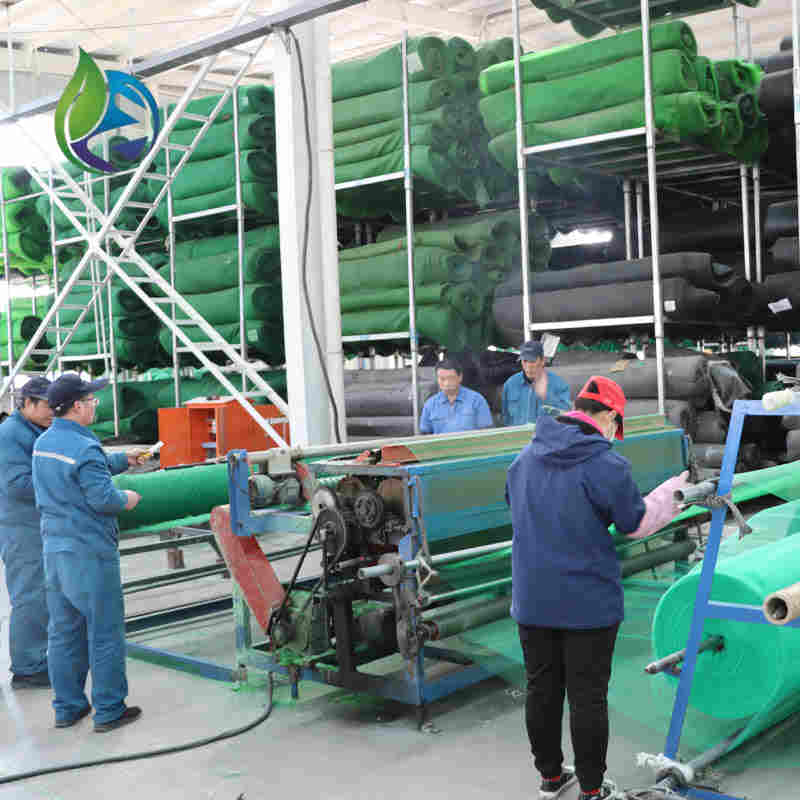
The production of 3D Geomat for erosion control follows controlled industrial processes:
Polymer raw material selection and blending with stabilizers
Extrusion of continuous filaments using multi-nozzle extrusion equipment
Random laying and spatial bonding to form 3D structure
Thermal welding or calendaring for dimensional stability
Online thickness and weight inspection
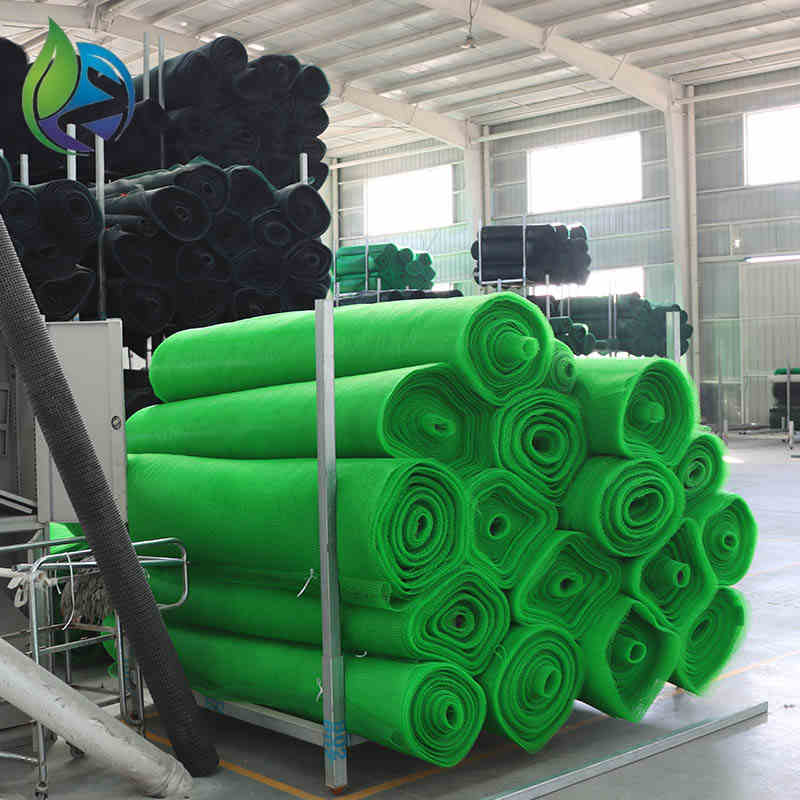
Roll cutting, packaging, and batch traceability labeling
Product Definition
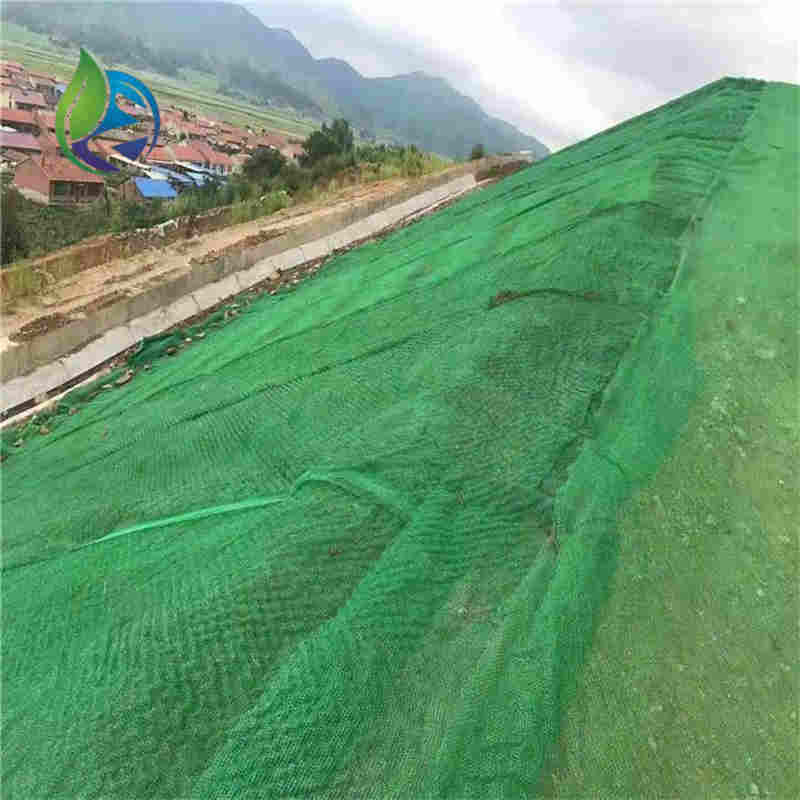
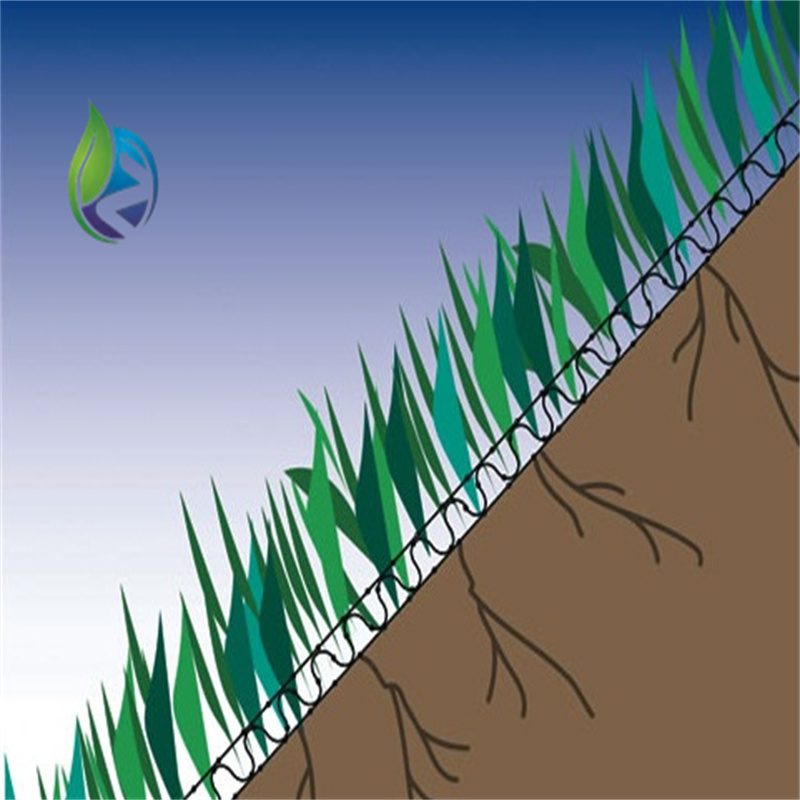
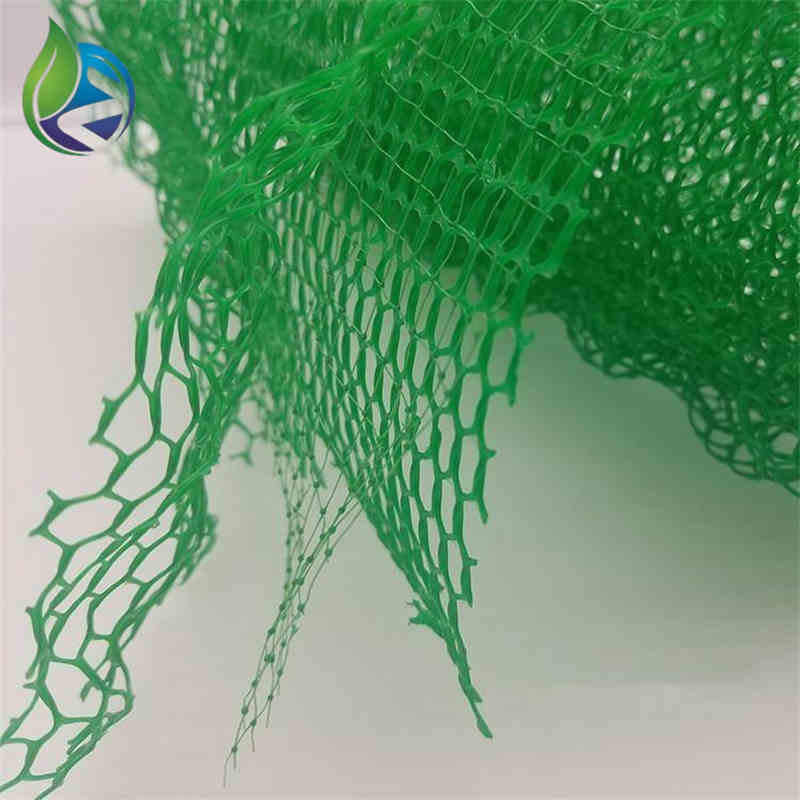
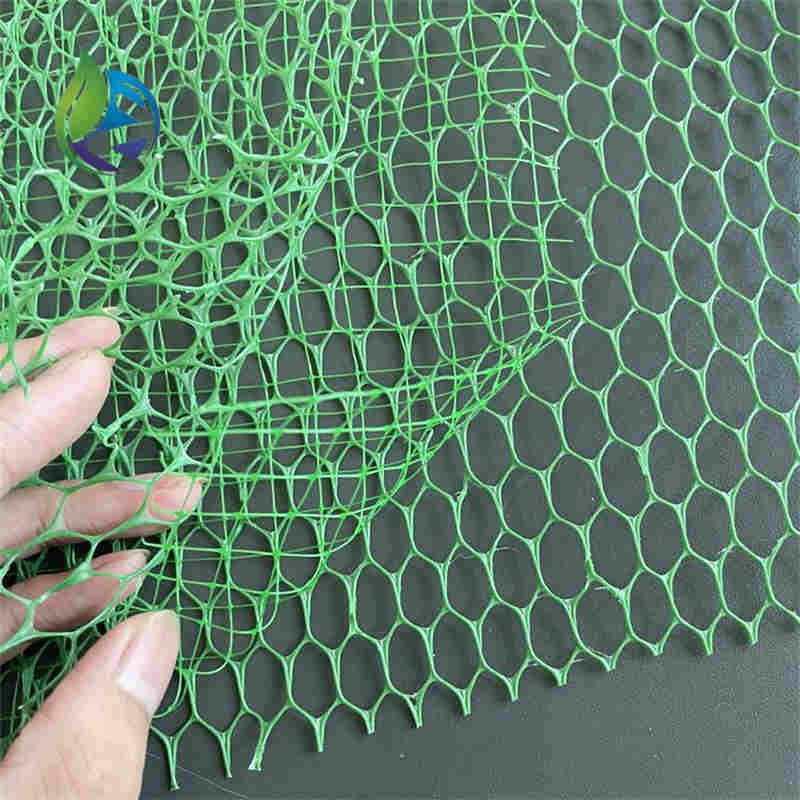
3D Geomat for erosion control is a three-dimensional synthetic polymer mat designed to stabilize soil surfaces, protect slopes from water and wind erosion, and promote vegetation growth by forming a permanent reinforcement layer.
Technical Parameters and Specifications
The following specifications represent commonly adopted engineering-grade parameters for 3D Geomat systems:
Thickness: 10 mm – 20 mm
Unit weight: 250 g/m² – 500 g/m²
Material: UV-stabilized polypropylene (PP) or polyethylene (PE)
Tensile strength: ≥ 1.2 kN/m (MD/TD)
Elongation at break: ≥ 30%
Operating temperature range: -40°C to +80°C
Design service life: ≥ 20 years (soil-buried conditions)
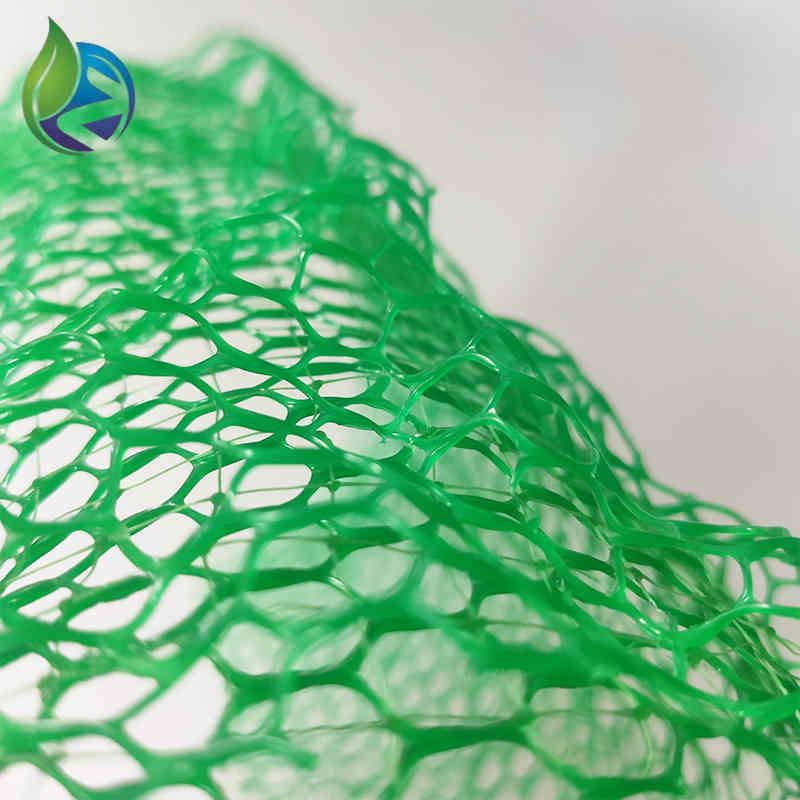
Structure and Material Composition
The performance of 3D Geomat for erosion control is driven by its engineered spatial structure:
Upper Layer: Randomly oriented polymer filaments forming surface protection
Middle Layer: Interlocked three-dimensional mesh providing soil anchorage
Bottom Layer: Open structure enabling root penetration and water infiltration
Material Additives: UV inhibitors, anti-aging stabilizers
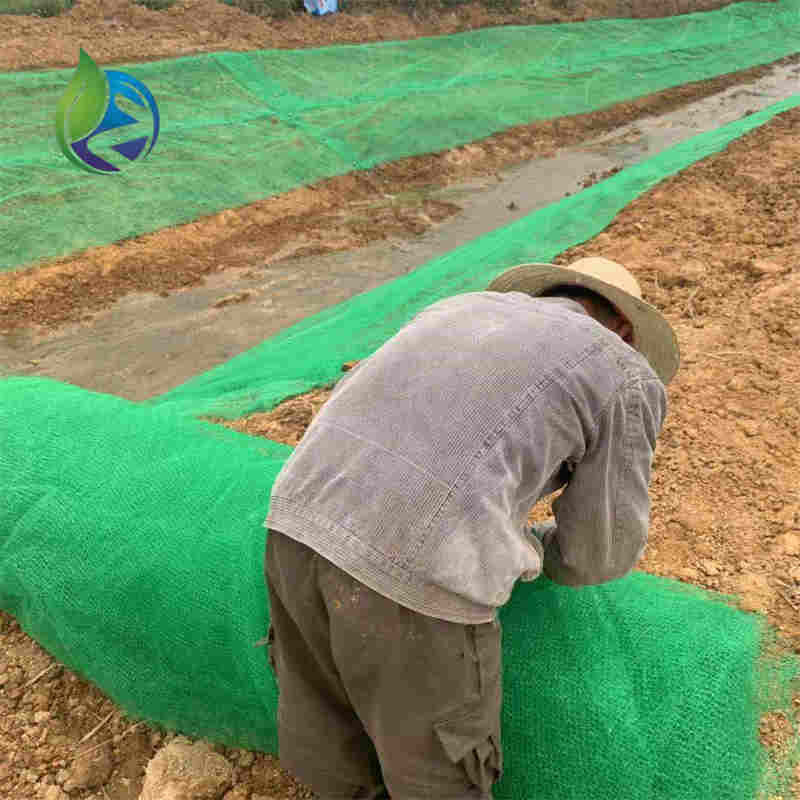
Manufacturing Process
The production of 3D Geomat for erosion control follows controlled industrial processes:
Polymer raw material selection and blending with stabilizers
Extrusion of continuous filaments using multi-nozzle extrusion equipment
Random laying and spatial bonding to form 3D structure
Thermal welding or calendaring for dimensional stability
Online thickness and weight inspection
Roll cutting, packaging, and batch traceability labeling
Industry Comparison
| Material Type | Erosion Resistance | Vegetation Support | Service Life | Installation Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3D Geomat | High | Excellent | 20+ years | Moderate |
| Geotextile Fabric | Medium | Limited | 10–15 years | Low |
| Concrete Slope Protection | Very High | None | 30+ years | High |
| Natural Fiber Mat | Low | Good (short-term) | 1–3 years | Low |
Application Scenarios
3D Geomat for erosion control is widely adopted by:
Highway and railway slope protection projects
Hydraulic engineering and riverbank stabilization
Mining rehabilitation and landfill capping
Municipal landscaping and green infrastructure
Industrial parks and EPC earthwork projects
Core Pain Points and Solutions
Pain Point: Soil loss on steep slopes
Solution: 3D structure provides mechanical anchoragePain Point: Poor vegetation survival
Solution: Open matrix retains moisture and seedsPain Point: UV degradation of materials
Solution: UV-stabilized polymersPain Point: High maintenance costs
Solution: Long service life with minimal intervention
Risk Warnings and Mitigation
Potential risks and corresponding mitigation measures include:
Improper anchoring: use specified steel or polymer anchors
Inadequate overlap: maintain ≥100 mm overlap between rolls
Exposure before backfilling: limit UV exposure during installation
Incorrect slope preparation: ensure compacted and graded subgrade
Procurement and Selection Guide
Define slope gradient and hydraulic conditions
Select appropriate thickness and unit weight
Verify polymer type and UV resistance
Check compliance with project specifications
Request laboratory test reports
Evaluate supplier manufacturing capability
Confirm logistics and roll dimensions
Engineering Case Study
In a highway slope stabilization project, 3D Geomat for erosion control with 15 mm thickness was installed on a 35° embankment slope. After hydroseeding and six months of growth, vegetation coverage exceeded 90%, with no visible soil erosion during seasonal rainfall.
FAQ
What is the main function of 3D Geomat? Soil stabilization and erosion prevention.
Can it be used underwater? Yes, with proper anchoring.
Is vegetation mandatory? Recommended for optimal performance.
Does it replace concrete? No, it is an ecological alternative.
What slopes are suitable? Typically up to 45°.
Is UV resistance required? Yes, for exposed conditions.
Can it be combined with geotextiles? Yes, in layered systems.
How is it installed? Anchoring + backfilling + seeding.
What is the roll width? Commonly 2–4 meters.
Is testing required before use? Recommended for major projects.
Call to Action
For project-specific pricing, technical datasheets, or engineering samples of 3D Geomat for erosion control, please submit your inquiry to our technical sales team.
E-E-A-T Author Statement
This article is prepared by a geosynthetics engineering team with over 15 years of experience in erosion control, slope stabilization, and infrastructure material selection for EPC and civil engineering projects worldwide.